Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) is a treatment option in the initial management of patients with brain metastases. While its efficacy has been demonstrated in several prior studies, treatment-related complications, particularly symptomatic radiation necrosis (RN), remains as an obstacle for wider implementation of this treatment modality. We thus examined risk factors associated with the development of symptomatic RN in patients treated with SRS for brain metastases.
Patients and methodsWe performed a retrospective review of our institutional database to identify patients with brain metastases treated with SRS. Diagnosis of symptomatic RN was determined by appearance on serial MRIs, MR spectroscopy, requirement of therapy, and the development of new neurological complaints without evidence of disease progression.
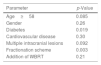
ResultsWe identified 323 brain metastases treated with SRS in 170 patients from 2009 to 2018. Thirteen patients (4%) experienced symptomatic RN after treatment of 23 (7%) lesions. After SRS, the median time to symptomatic RN was 8.3 months. Patients with symptomatic RN had a larger mean target volume (p<0.0001), and thus larger V100% (p<0.0001), V50% (p<0.0001), V12Gy (p<0.0001), and V10Gy (p=0.0002), compared to the rest of the cohort. Single-fraction treatment (p=0.0025) and diabetes (p=0.019) were also significantly associated with symptomatic RN.
ConclusionSRS is an effective treatment option for patients with brain metastases; however, a subset of patients may develop symptomatic RN. We found that patients with larger tumor size, larger plan V100%, V50%, V12Gy, or V10Gy, who received single-fraction SRS, or who had diabetes were all at higher risk of symptomatic RN.
La radiocirugía estereotáctica (RCE) es una opción de tratamiento en el tratamiento inicial de pacientes con metástasis cerebrales. Aunque su eficacia ha quedado demostrada en varios estudios previos, las complicaciones relacionadas con el tratamiento, en particular la necrosis por radiación (NR) sintomática, siguen siendo un obstáculo para una aplicación más generalizada de esta modalidad de tratamiento. Así pues, examinamos los factores de riesgo asociados al desarrollo de NR sintomática en pacientes tratados con RCE para metástasis cerebrales.
Pacientes y métodosRealizamos una revisión retrospectiva de nuestra base de datos institucional para identificar pacientes con metástasis cerebrales tratados con RCE. El diagnóstico de NR sintomática se determinó por la aparición en resonancias magnéticas en serie, espectroscopia por resonancia magnética, la necesidad de tratamiento y el desarrollo de nuevas quejas neurológicas, sin signos de progresión de la enfermedad.
ResultadosIdentificamos 323 metástasis cerebrales tratadas con RCE en 170 pacientes, entre 2009 y 2018. Trece pacientes (4%) experimentaron NR sintomática después del tratamiento de 23 (7%) lesiones. Después de la RCE, la mediana de tiempo hasta la aparición de NR sintomática fue de 8,3 meses. Los pacientes con NR sintomática tuvieron un volumen objetivo medio mayor (p < 0,0001), y por lo tanto, mayor V100% (p < 0,0001), V50% (p < 0,0001), V12 Gy (p < 0,0001), y V10 Gy (p = 0,0002), en comparación con el resto de la cohorte. El tratamiento de una sola fracción (p = 0,0025) y la diabetes (p = 0,019) también se asociaron significativamente a NR.
ConclusiónLa RCE es una opción de tratamiento eficaz para los pacientes con metástasis cerebrales; sin embargo, un subconjunto de pacientes puede desarrollar NR sintomática. Observamos que los pacientes con un mayor tamaño de tumor, un plan V100%, V50%, V12 Gy o V10 Gy mayor, que recibieron RCE de una sola fracción o que tenían diabetes, presentaban un mayor riesgo de padecer NR sintomática.
Article

If it is the first time you have accessed you can obtain your credentials by contacting Elsevier Spain in suscripciones@elsevier.com or by calling our Customer Service at902 88 87 40 if you are calling from Spain or at +34 932 418 800 (from 9 to 18h., GMT + 1) if you are calling outside of Spain.
If you already have your login data, please click here .
If you have forgotten your password you can you can recover it by clicking here and selecting the option ¿I have forgotten my password¿.