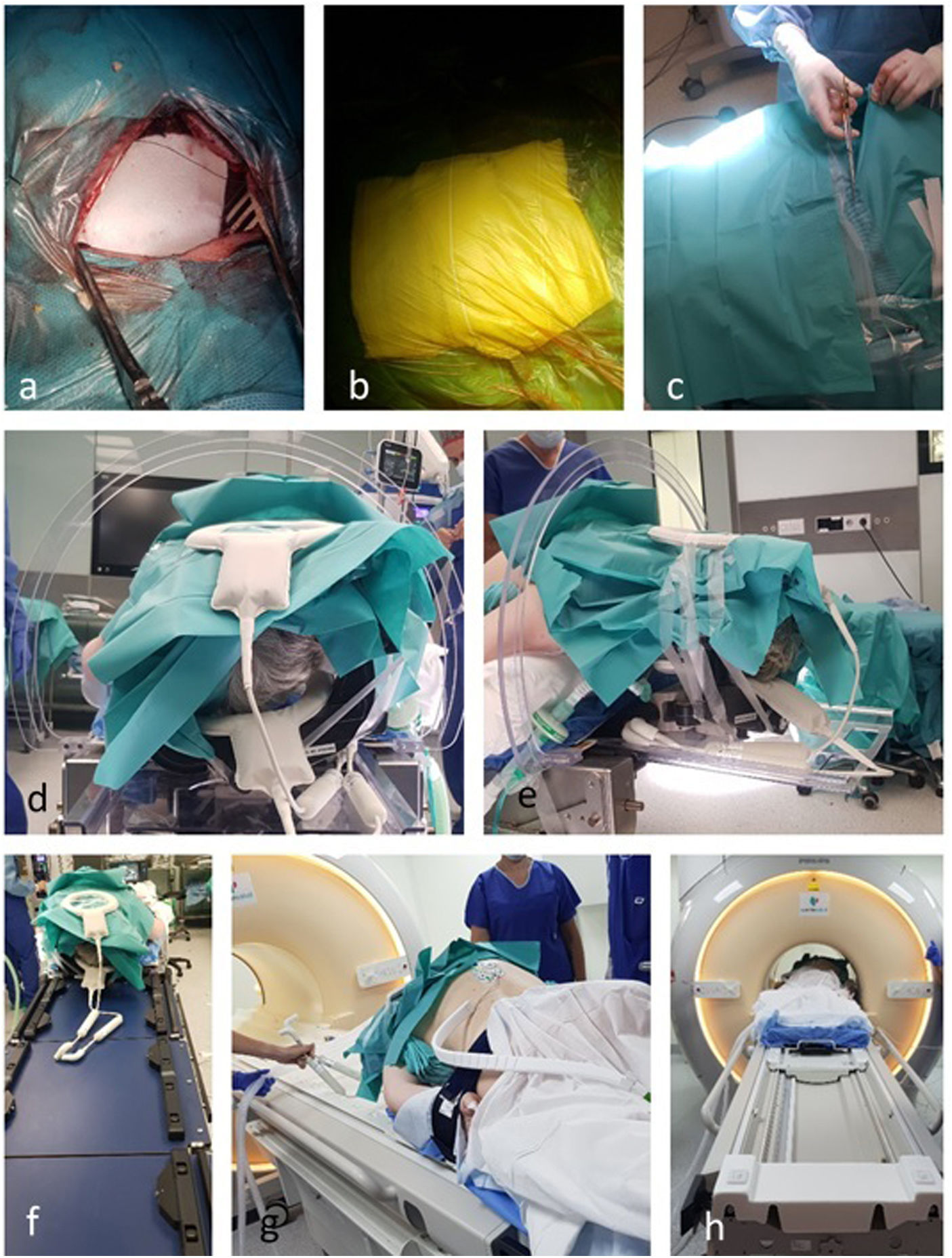
Intraoperative MRI (ioMRI) consists of performing a MRI during brain or spinal surgery. Although it is a safe and useful technique, it is available in a few hospitals. This means some aspects are not perfectly defined or standardized, forcing each center to develop its own solutions. Our goal is to describe the technique, evaluate the changes made to optimize its use and thus be able to facilitate the intraoperative resonance implementation in other neurosurgery departments.
MethodsA prospective analysis of patients consecutively operated using high-field ioMRI guidance was carried out, describing the type of tumor, clinical data, time and sequences of ioMR, use of intraoperative neurophysiology, preoperative tumor volume, after ioMR, and postoperative, as well as complications.
ResultsioMR was performed in 38 patients selected from among 425 brain tumors (9%) operated on in this interval. The tumor types were: 11 glioblastomas, 8 anaplastic astrocytomas, 5 diffuse astrocytomas, 4 meningiomas, 3 oligodendrogliomas, 2 metastases, 2 epidermoid cysts, 1 astroblastoma, 1 arachnoid cyst and 1 pituitary adenoma.
The mean age was 45 years. The mean preoperative tumor volume was 45.22cc, after the ioMR 5.08cc and postoperative 1.28cc.
Resection was extended after ioMR in 76%. Gross total resection was achieved in 15 patients and residual tumor of less than 1cc was observed in 8. An intentional tumor tissue was left in an eloquent brain region (mean volume 7cc) in 13 patients.
Bleeding and ischemia complications were detected early on ioMR in 5%.
MRI length was 47 min on average.
ConclusionsIntraoperative MRI was a useful and safe technique, and no associated complications were registered.
La RM intraoperatoria (RMio) consiste en la realización de una resonancia durante la cirugía de una lesión cerebral o espinal. Es una técnica segura y útil, aunque está disponible en pocos hospitales y algunos aspectos no están perfectamente definidos ni estandarizados, por lo que cada centro elabora sus propias soluciones. Nuestro objetivo es describir la técnica utilizada para la realización de RMio, evaluar los cambios que se han ido realizando para optimizar su uso desde el comienzo y así poder facilitar la puesta en marcha de una resonancia intraooperatoria en otros departamentos de neurocirugía.
Material y métodosEstudio prospectivo de pacientes intervenidos consecutivamente con RMio, describiendo el tipo de tumor, datos clínicos, tiempo y secuencias de RMio, empleo de neurofisiología intraoperatoria, volumen tumoral preoperatorio, tras la RMio, y postoperatorio, y complicaciones observadas.
ResultadosSe realizó RMio en 38 pacientes seleccionados de los 425 tumores cerebrales (9%) operados en este intervalo. Los tipos tumorales fueron: 11 glioblastomas, 8 astrocitomas anaplásicos, 5 astrocitomas difusos, 4 meningiomas, 3 oligodendrogliomas, 2 metástasis, 2 quistes epidermoides, 1 astroblastoma, 1 quiste aracnoideo y 1 adenoma hipofisario.
La edad media fue 45 años. El volumen tumoral preoperatorio medio fue 45,22cc, tras la RMio de 5,08 cc y el postoperatorio 1,28 cc.
En el 76% se amplió la resección tras la RMio. En 15 pacientes se consiguió una resección completa y en 8 se objetivó un resto menor de 1cc. En 13 pacientes se dejó un resto intencional en área elocuente o regiones de base de cráneo (volumen medio 7cc).
En un 5% se detectaron complicaciones de sangrado e isquemia de forma precoz en la RMio.
La realización de la RMio requirió una media de 47 minutos.
ConclusionesLa RMio resultó una técnica útil y segura sin registrarse complicaciones relacionadas con su realización.
Article

If it is the first time you have accessed you can obtain your credentials by contacting Elsevier Spain in suscripciones@elsevier.com or by calling our Customer Service at902 88 87 40 if you are calling from Spain or at +34 932 418 800 (from 9 to 18h., GMT + 1) if you are calling outside of Spain.
If you already have your login data, please click here .
If you have forgotten your password you can you can recover it by clicking here and selecting the option ¿I have forgotten my password¿.