Epidural infiltrations are used for treatment of low back pain and sciatica. Linked to lumbar radiculopathy (lumbosacral radicular syndrome). This study evaluates the efficacy of epidural infiltration by different routes to reduce pain intensity, disability and return to work.
MethodsIs a prospective observational study in one hundred consecutive patients sent to pain unit for severe lumbo-sacral radiculopaty. We analyze the efficacy on pain relief (Visual Analogue Scale) and funcional status at two weeks, one month, and three months after epidural injection of local anesthetics and esteroids with differents approachs (interlaminar, caudal and transforaminal).
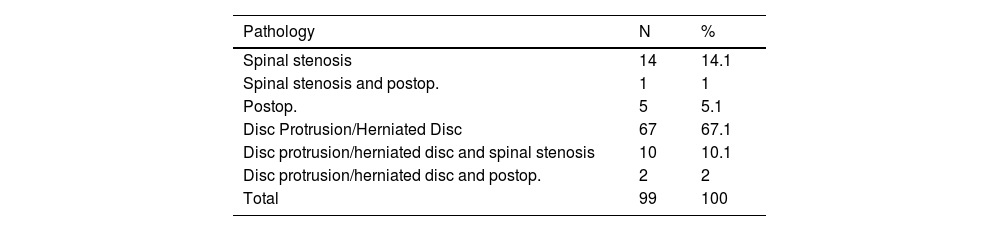
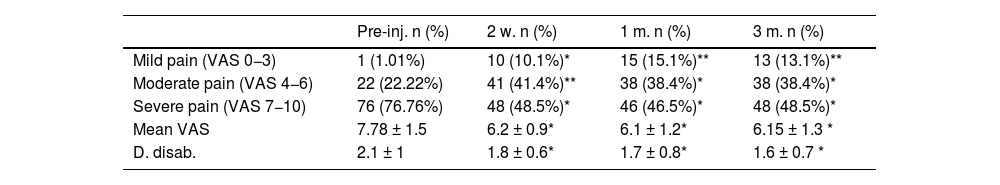
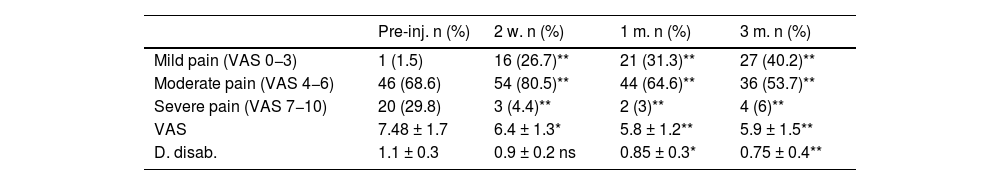
ResultsNinety nine patients (46.5% men, 53.5 women) were finally enrrolled in the study. Mean age was 57.47 ± 11.1 years. The caudal approach was used in 58.6% patients, 23.2% transforaminal approach, and 18.2% interlaminar approach. A significant pain relief was found in all times studied (EAV 7.48 ± 1.5 basal; 6.2 ± 0,9 at 15 days; 6.3 ± 1.2 at one month; 6.15 ± 1.3 at 3 months, p < 0.05). Transforaminal approach was superior to caudal or interlaminal. Seventy percent in time off work patients returned to work after epidural inyections.
ConclusionsEpidural local anesthetics with esteroids injections for lumbo-sacral radiculopathy were effective for low back pain, improved functional status and promoted return to work. Transforaminal approach is superior to others.
Las infiltraciones epidurales (IEE) constituyen una alternativa en el tratamiento del síndrome de radiculopatía lumbosacro (SRL). El objetivo de estudio es evaluar la eficacia de las IEE en la intensidad del dolor, mejora de la recuperación funcional y retorno a la actividad laboral.
Material y métodosSe realizó un estudio prospectivo en una cohorte de cien pacientes consecutivos remitidos a la unidad del dolor por SRL de más de 3 meses de duración. Se analizó la eficacia de las inyecciones de corticoides y anestésicos locales por diferentes vías (interlaminar, caudal y transforaminal) a los 15 dias, 1 mes y 3 meses de la infiltración, en cuanto a la intensidad del dolor mediante la Escala Analóga Visual (EAV), evolución del grado de discapacidad y la reincorporación laboral.
ResultadosNoventa y nueve pacientes se incluyeron en el estudio. El 46,5% fueron varones y 53,5% mujeres. La edad media fue de 57,47 ± 11,1 años. En la mayoría (58,6%) de los casos se optó por la vía caudal, seguida de la transforaminal (23,2%), e interlaminar (18,2%). Las IEE produjeron una reducción significativa del dolor en todos los periodos estudiados (EAV 7,78 ± 1,5 basal; 6,2 ± 0,9 a los 15 días; 6,3 ± 1,2 al mes; 6,15 ± 1,3 a los 3 meses, p < 0.05). La vía de acceso más eficaz fue la transforaminal. El 70% de los pacientes en situación de incapacidad laboral retornaron a su trabajo tras el tratamiento.
Discusión y ConclusionesEl tratamiento mediante IEE redujo la intensidad del dolor por SRL, mejoró la situación funcional y la reincorporación a la actividad laboral.
Article

If it is the first time you have accessed you can obtain your credentials by contacting Elsevier Spain in suscripciones@elsevier.com or by calling our Customer Service at902 88 87 40 if you are calling from Spain or at +34 932 418 800 (from 9 to 18h., GMT + 1) if you are calling outside of Spain.
If you already have your login data, please click here .
If you have forgotten your password you can you can recover it by clicking here and selecting the option ¿I have forgotten my password¿.