Evaluar la utilidad del análisis del registro de la presión intracraneal (PIC) en el manejo de pacientes con marcada ventriculomegalia de larga evolución.
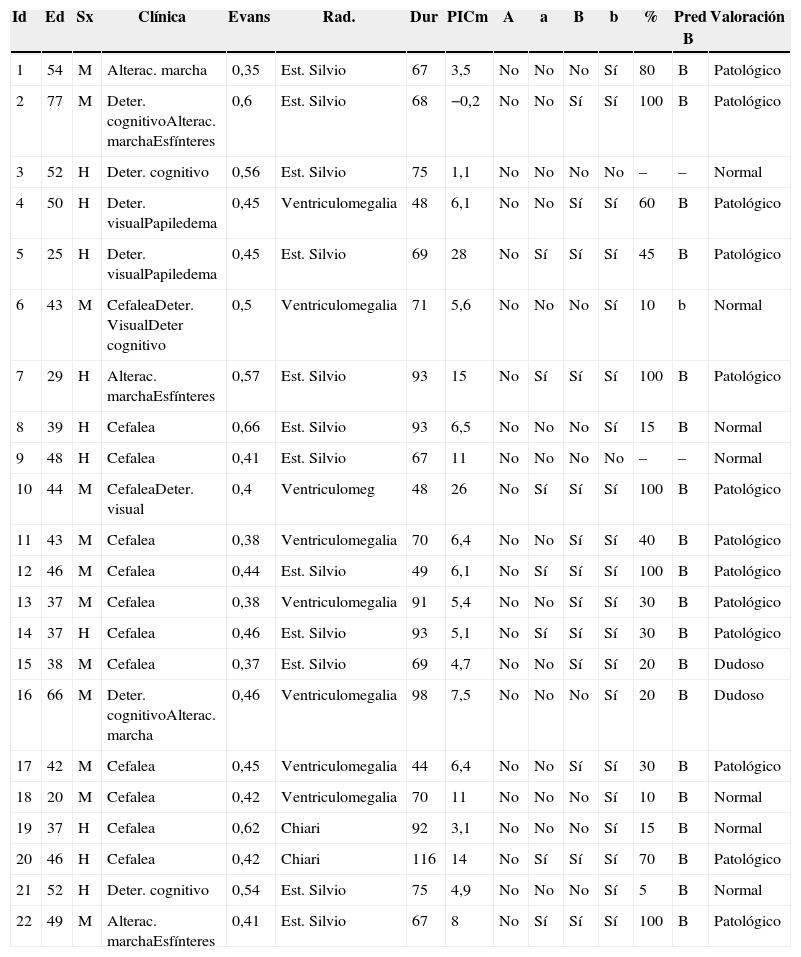
Material y métodosVeintidós pacientes con ventriculomegalia radiológica y clínica neurológica. Se recogen los datos demográficos, clínicos y radiológicos, así como los datos de monitorización de PIC y las complicaciones relacionadas con el procedimiento. Se evalúan resultados clínicos a los 6 meses de la intervención.
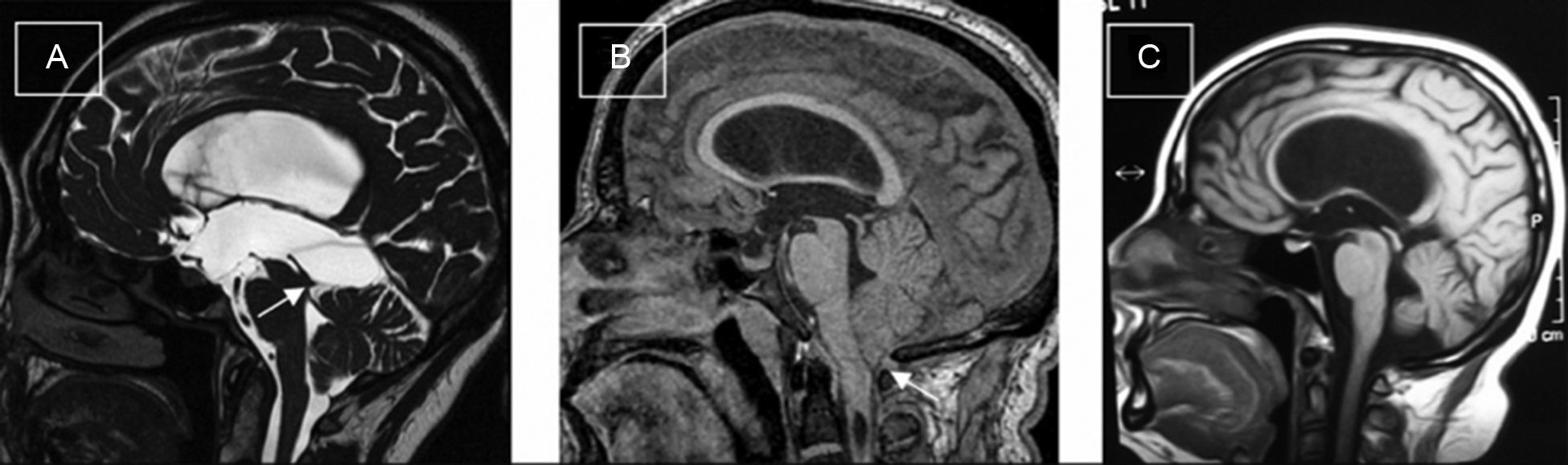
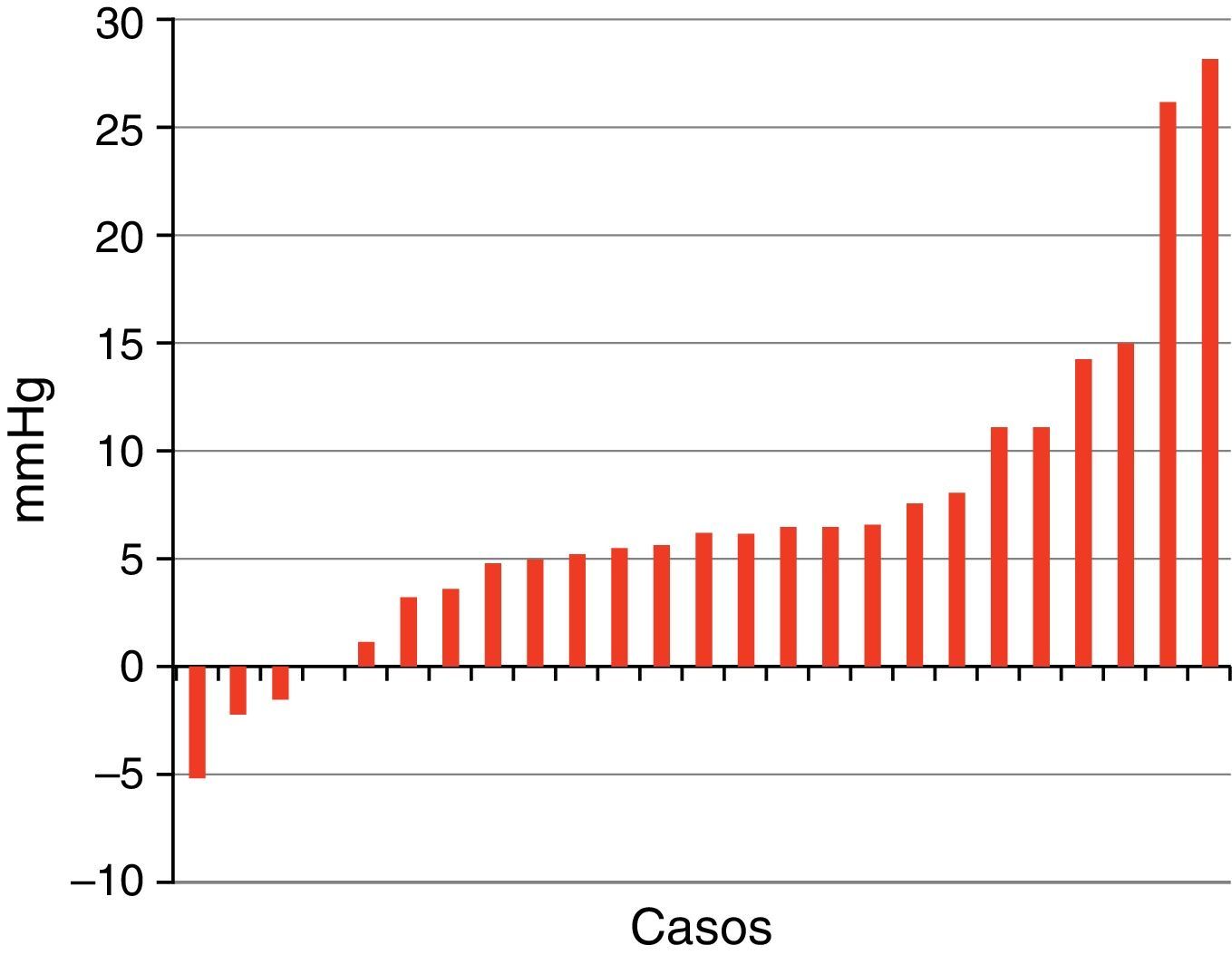
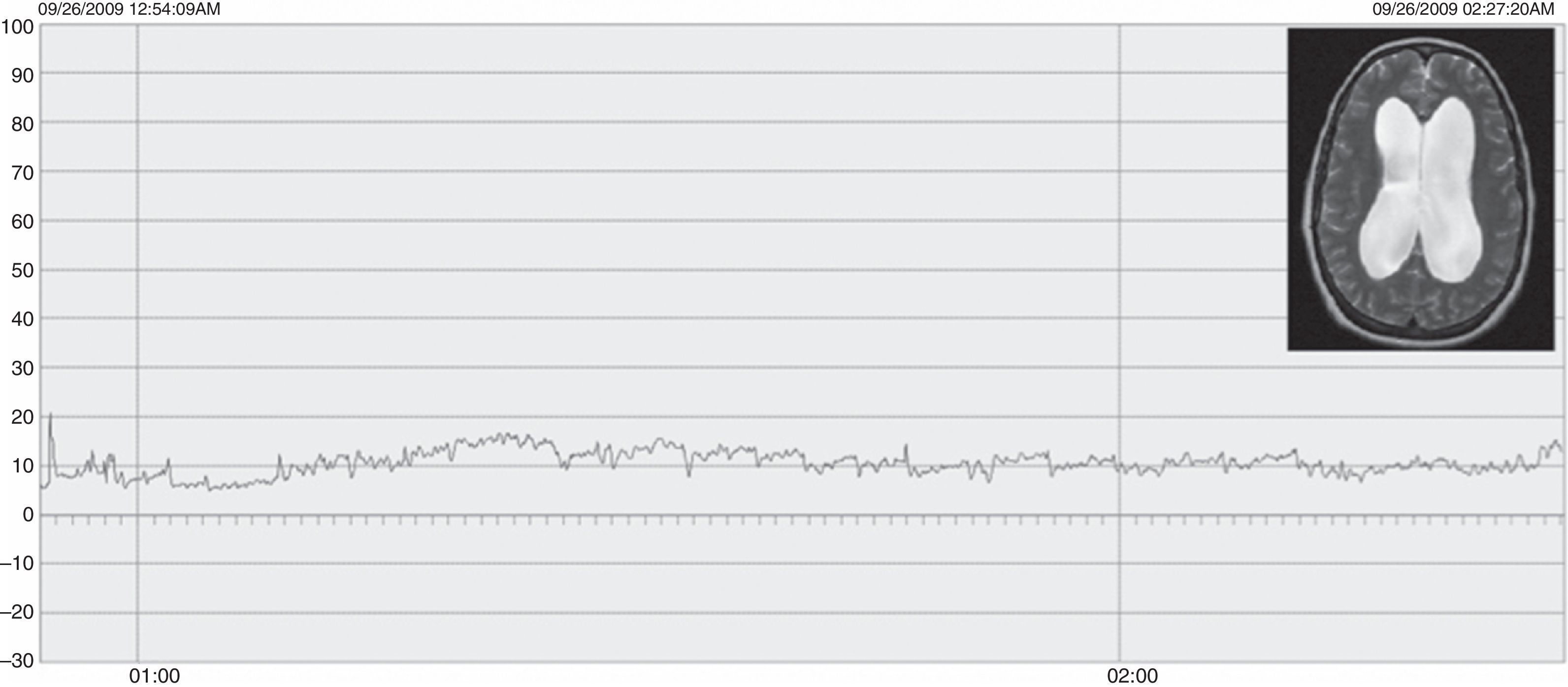
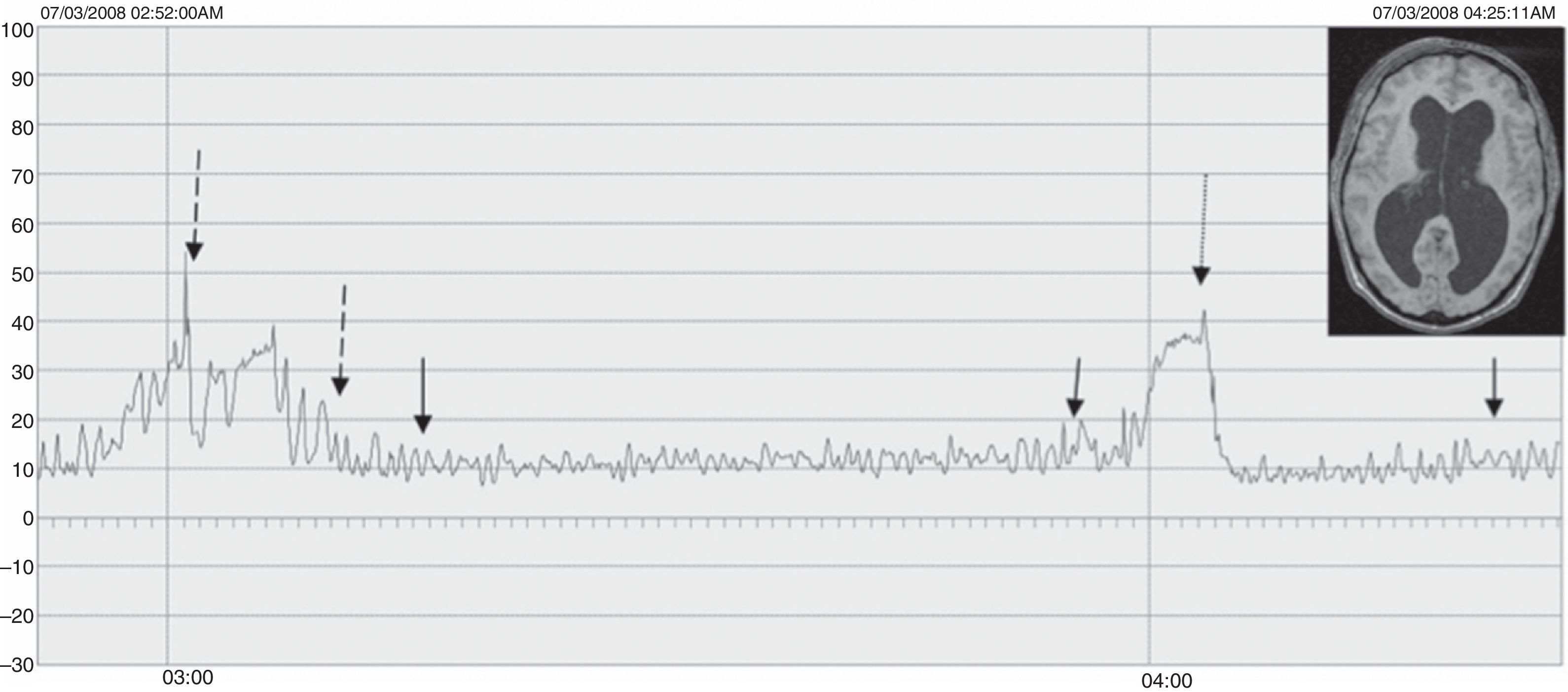
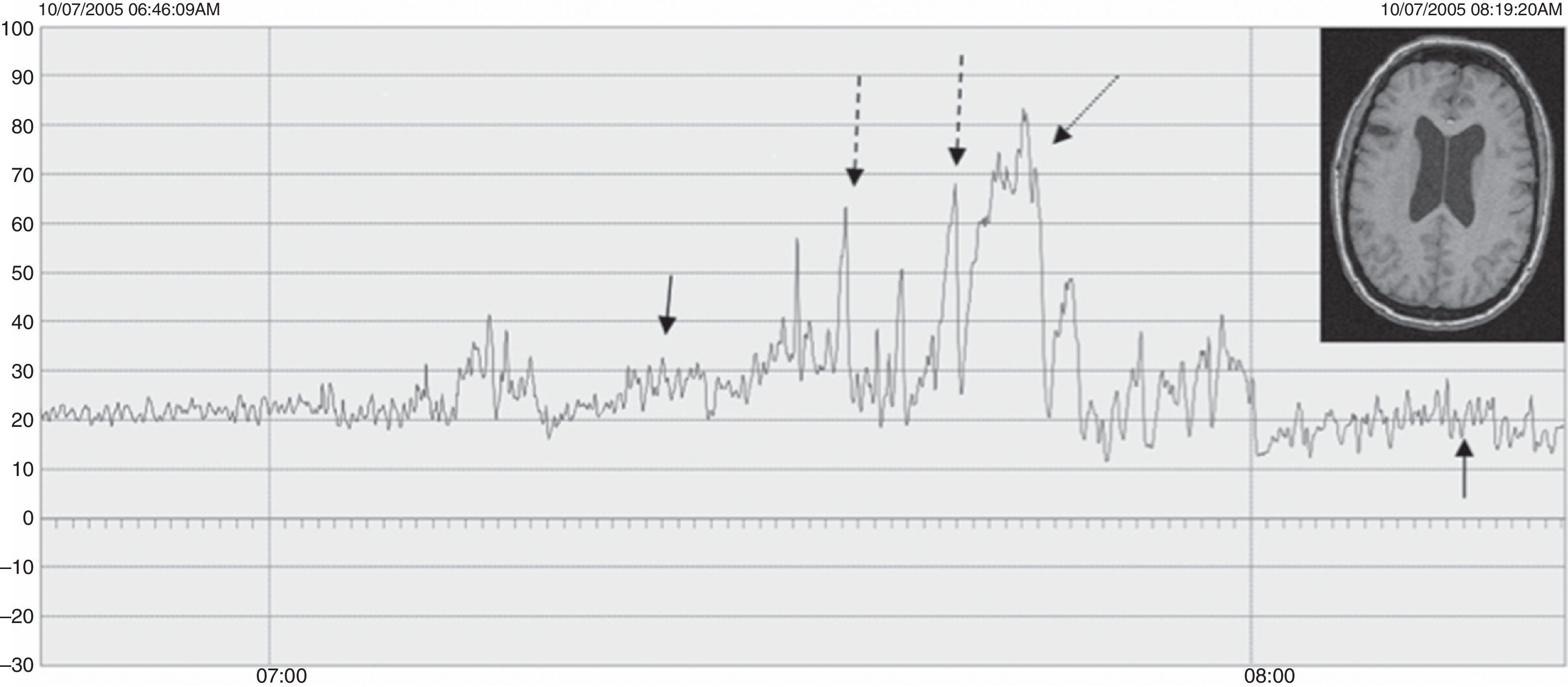
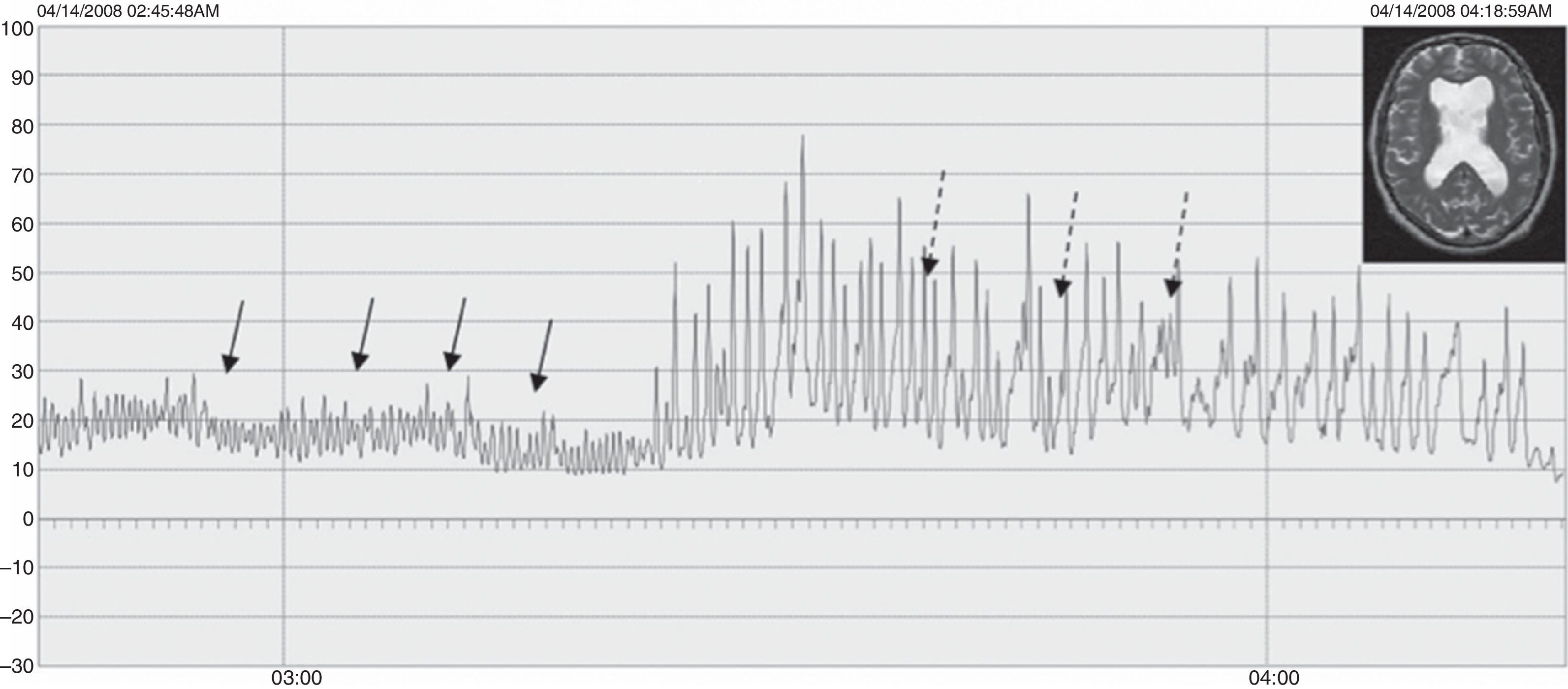
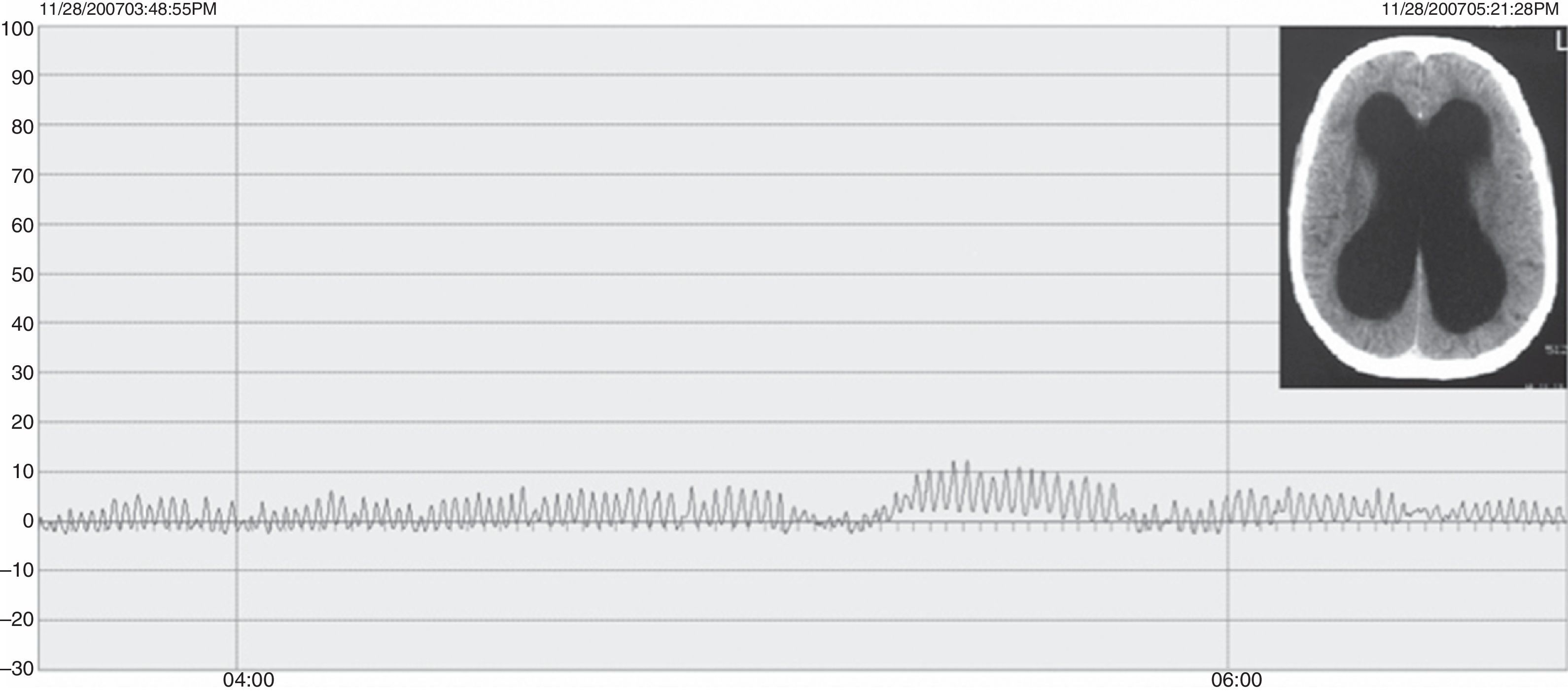
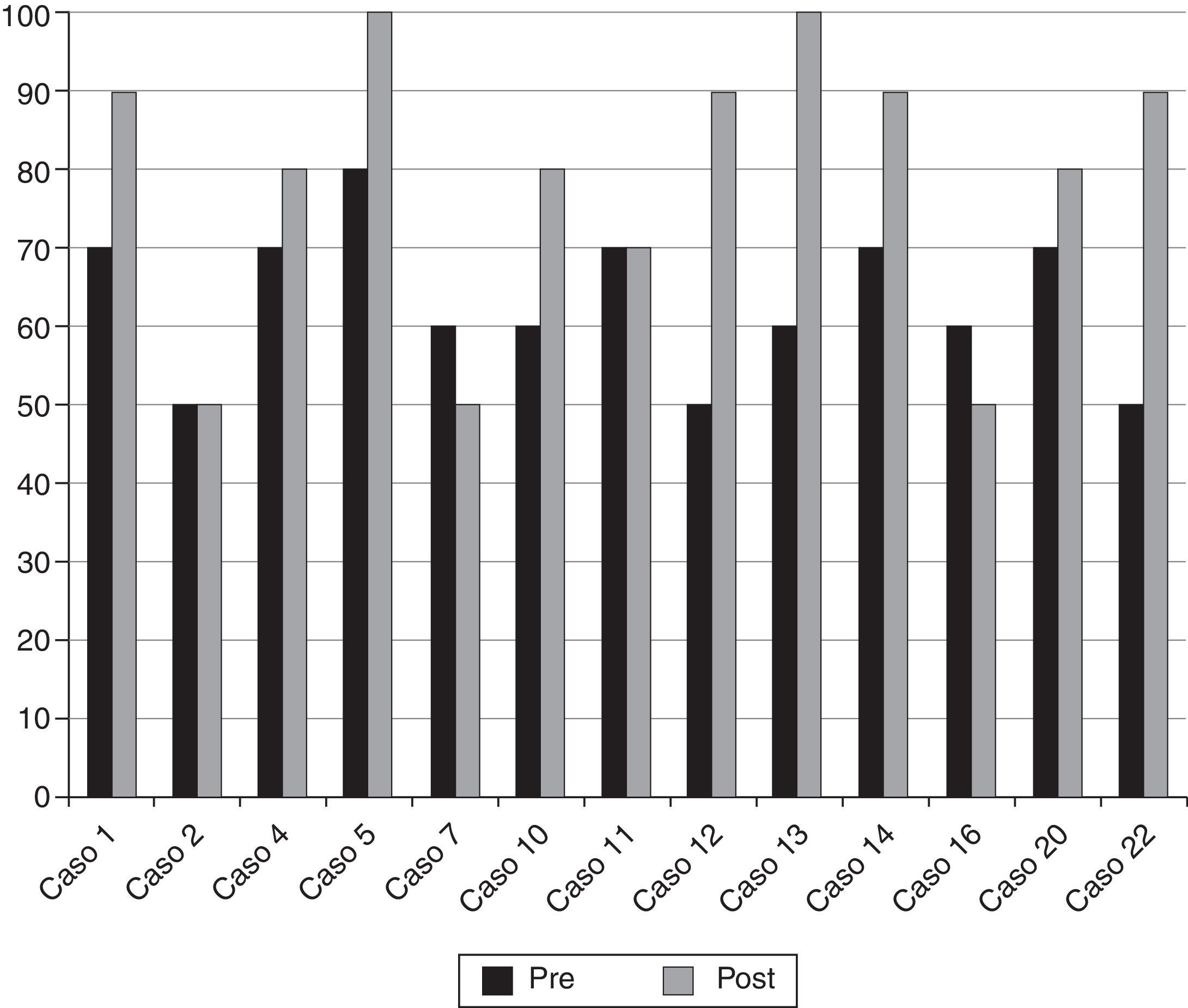
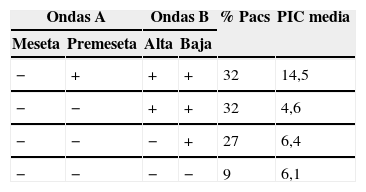
ResultadosLas edades oscilaron entre los 20 y los 70 años, con una media de 44 años. El síntoma de consulta más frecuente fue la cefalea. Los índices de Evans oscilaron entre 0,35 y 0,66, con una media de 0,47. El 55% asociaban estenosis de acueducto de Silvio. La PIC media fue superior a 12mmHg en solo el 9% de los pacientes, en tanto que el análisis morfológico de los trazados catalogó al 64% de los mismos como patológicos. El análisis morfológico del trazado evidencia ondas A premeseta en 7 pacientes y ondas B en 20 pacientes (14 de ellos con ondas B de alta amplitud). Se consideraron patológicos y por tanto candidatos a cirugía a 14 pacientes, de los que 12 aceptaron la intervención (derivación de líquido cefalorraquídeo o ventriculostomía). El 70% de ellos habían experimentado mejoría a los 6 meses. No hubo complicaciones relacionadas con la monitorización.
ConclusionesLa monitorización de la PIC es un método seguro y fiable, útil en el manejo de esta entidad, que permite seleccionar los pacientes candidatos a cirugía. Es imprescindible un análisis morfológico del trazado, ya que la PIC media es un dato de escasa utilidad, en tanto que la presencia de ondas A y B de alta amplitud se relaciona con una buena respuesta al shunt.
To analyze the usefulness of intracranial pressure (ICP) monitoring in overt long-standing ventriculomegaly patients.
Material and methodsThere were 22 patients with ventriculomegaly and neurological symptoms. Demographic, clinical and radiological data were collected, as well as ICP monitoring data and complications related to the procedure. Results were evaluated 6 months after surgery.
ResultsMean age was 44 years (22-70). Mean Evans index was 0.47 (0.35-0.66). Aqueductal stenosis was present in more than half of the patients (55%). Mean ICP was higher than 12mmHg in only 9% of patients. Morphological analysis of ICP recordings was abnormal in 64% of patients. “Pre-plateau” A waves were seen in 7 patients, with B waves seen in 20 patients (high amplitude B waves in 14). Twelve patients were operated on the basis of ICP recordings (CSF shunt or ventriculostomy). Seventy per cent of treated patients had improved at 6 months. There were no complications related to the monitoring technique.
ConclusionsICP monitoring is a valuable, safe tool, very useful in these cases. Selection of surgical candidates on the basis of ICP monitoring seems to be advisable. Mean ICP may be normal even with pathological recordings. Morphological analysis is essential to establish a correct diagnosis. The presence of A and B waves in the recording is highly related to good shunt response.
Article

If it is the first time you have accessed you can obtain your credentials by contacting Elsevier Spain in suscripciones@elsevier.com or by calling our Customer Service at902 88 87 40 if you are calling from Spain or at +34 932 418 800 (from 9 to 18h., GMT + 1) if you are calling outside of Spain.
If you already have your login data, please click here .
If you have forgotten your password you can you can recover it by clicking here and selecting the option ¿I have forgotten my password¿.