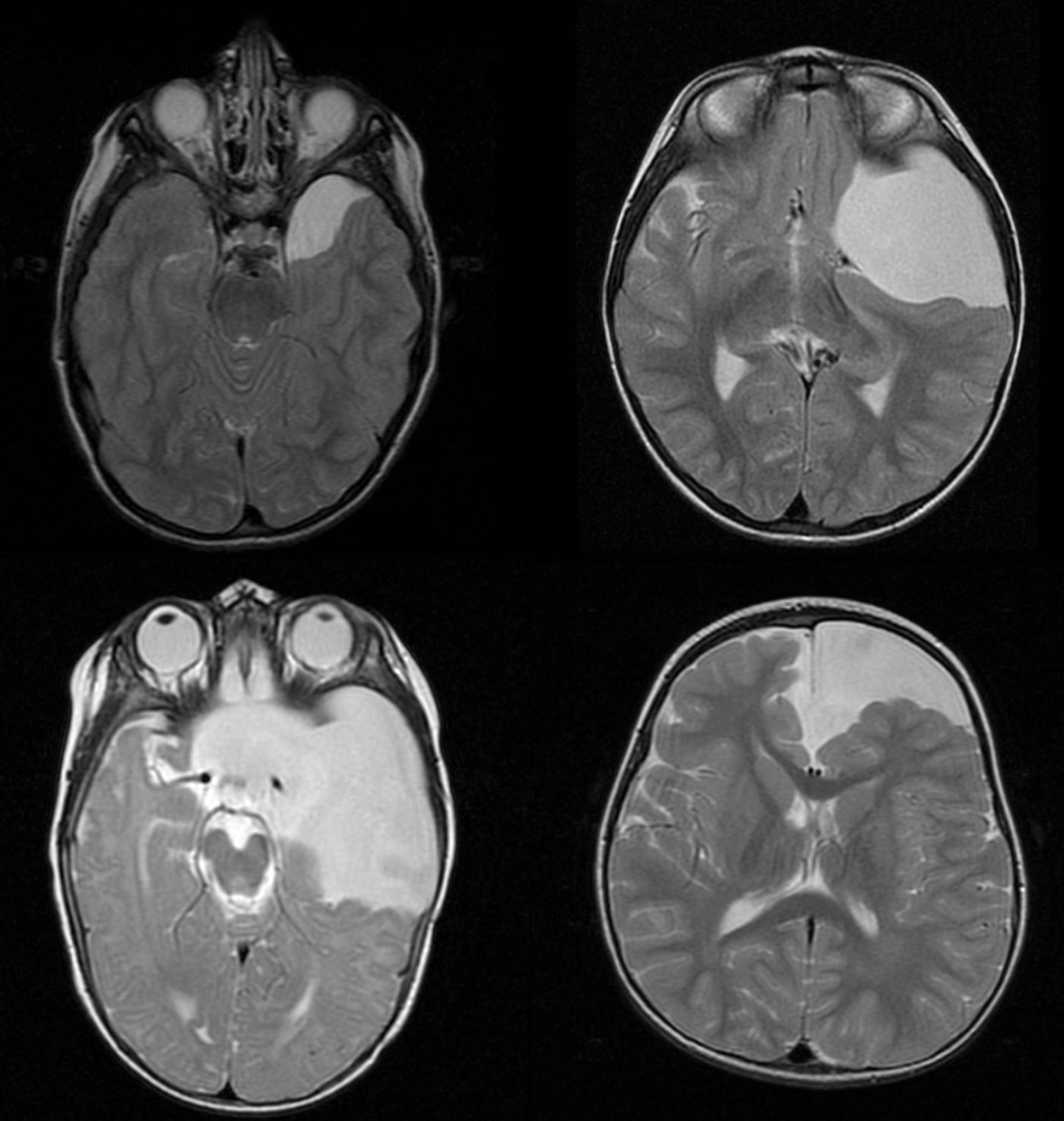
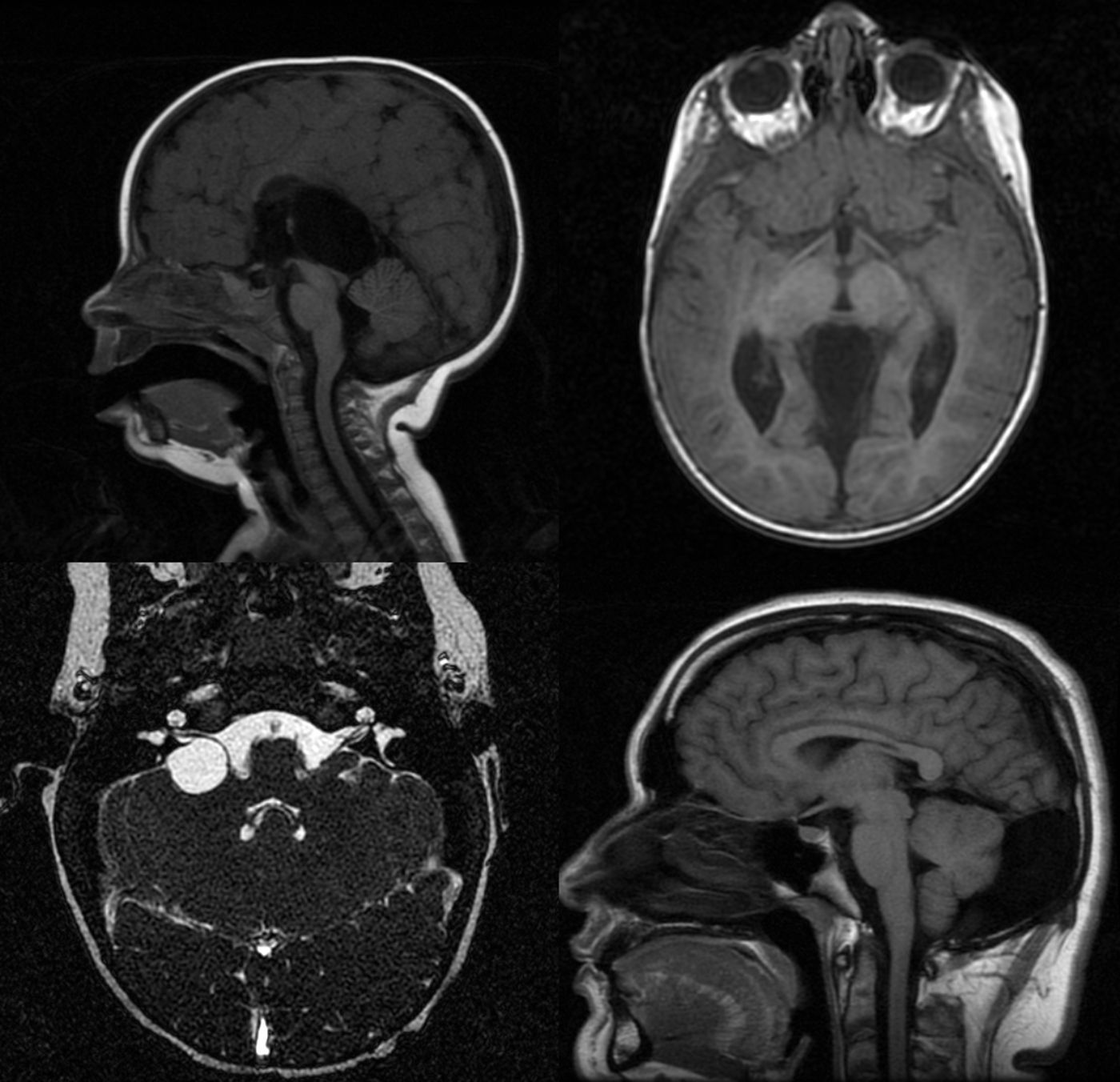
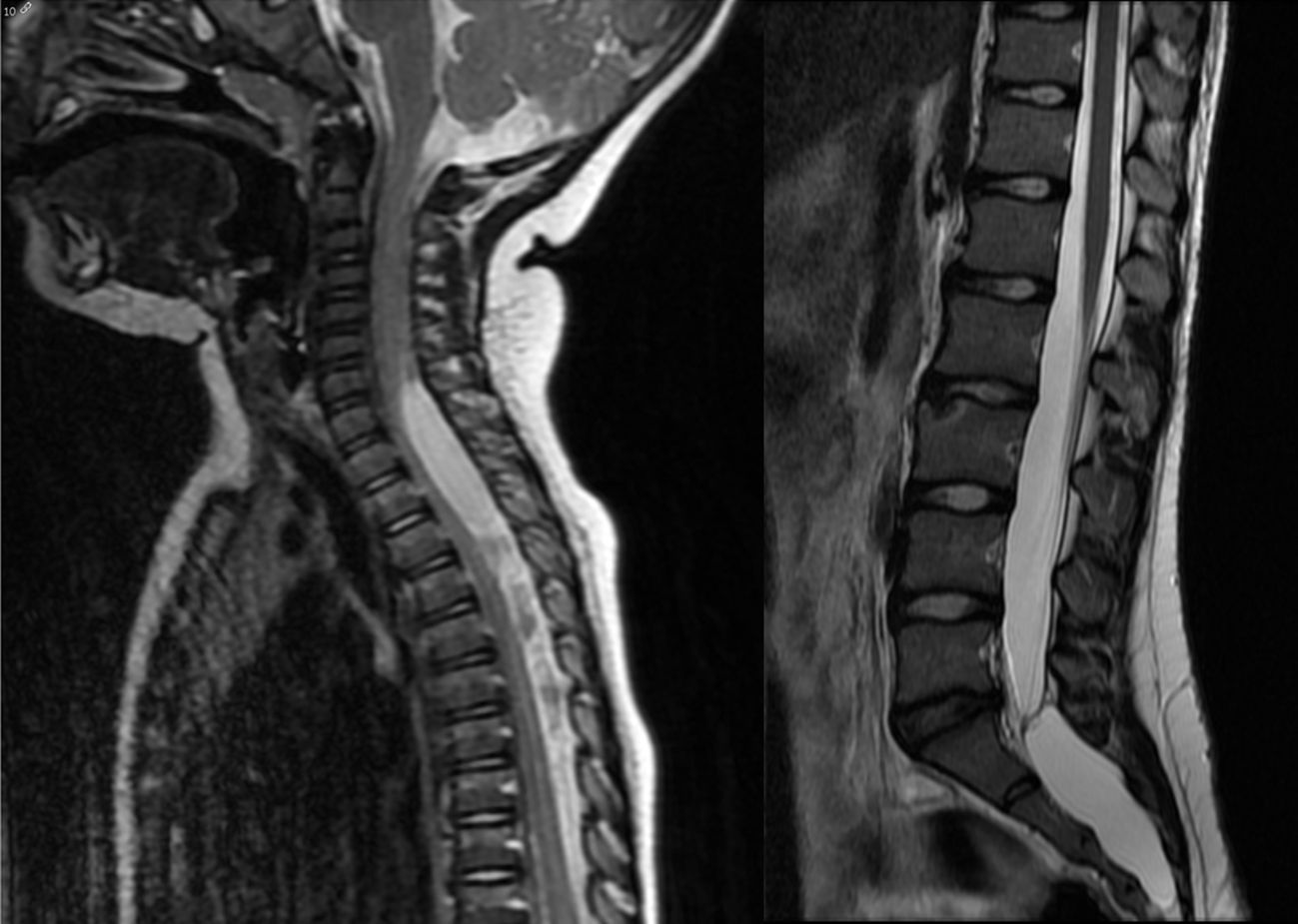
La prevalencia de los quistes aracnoideos en niños es del 1-3%. Son más frecuentes en el sexo masculino. Pueden localizarse tanto en el espacio intracraneal como a nivel espinal. Los intracraneales se clasifican en supratentoriales, infratentoriales y supra-infratentoriales. Los supratentoriales se subclasifican en de fosa media, hemisféricos de la convexidad, interhemisféricos, de la región selar e intraventriculares. Los infratentoriales se subdividen a su vez en supracerebelosos, infracerebelosos, hemisféricos, clivales y de ángulo pontocerebeloso. Por último, los espinales se clasifican según su localización extra o intradural y su afectación de raíces nerviosas.
The prevalence of arachnoid cysts in children is 1-3%. They are more frequent in boys. They can be located intracranially or in the spine. Intracranial cysts are classified as supratentorial, infratentorial, and supra-infratentorial (tentorial notch). Supratentorial are divided into middle cranial fossa, convexity, inter-hemisferic, sellar region, and intraventricular. Infratentorial are classified into supracerebellar, infracerebellar, hemispheric, clivus, and cerebellopontine angle. Finally spinal arachnoid cysts are classified taking into account whether they are extra- or intradural, and nerve root involvement.
Article

If it is the first time you have accessed you can obtain your credentials by contacting Elsevier Spain in suscripciones@elsevier.com or by calling our Customer Service at902 88 87 40 if you are calling from Spain or at +34 932 418 800 (from 9 to 18h., GMT + 1) if you are calling outside of Spain.
If you already have your login data, please click here .
If you have forgotten your password you can you can recover it by clicking here and selecting the option ¿I have forgotten my password¿.