Algunos estudios han señalado la posible influencia del posicionamiento postoperatorio de la cabecera sobre el riesgo de recurrencias y complicaciones médicas en los pacientes intervenidos por hematomas subdurales crónicos; sin embargo, esta hipótesis aún no se ha evaluado mediante un metaanálisis.
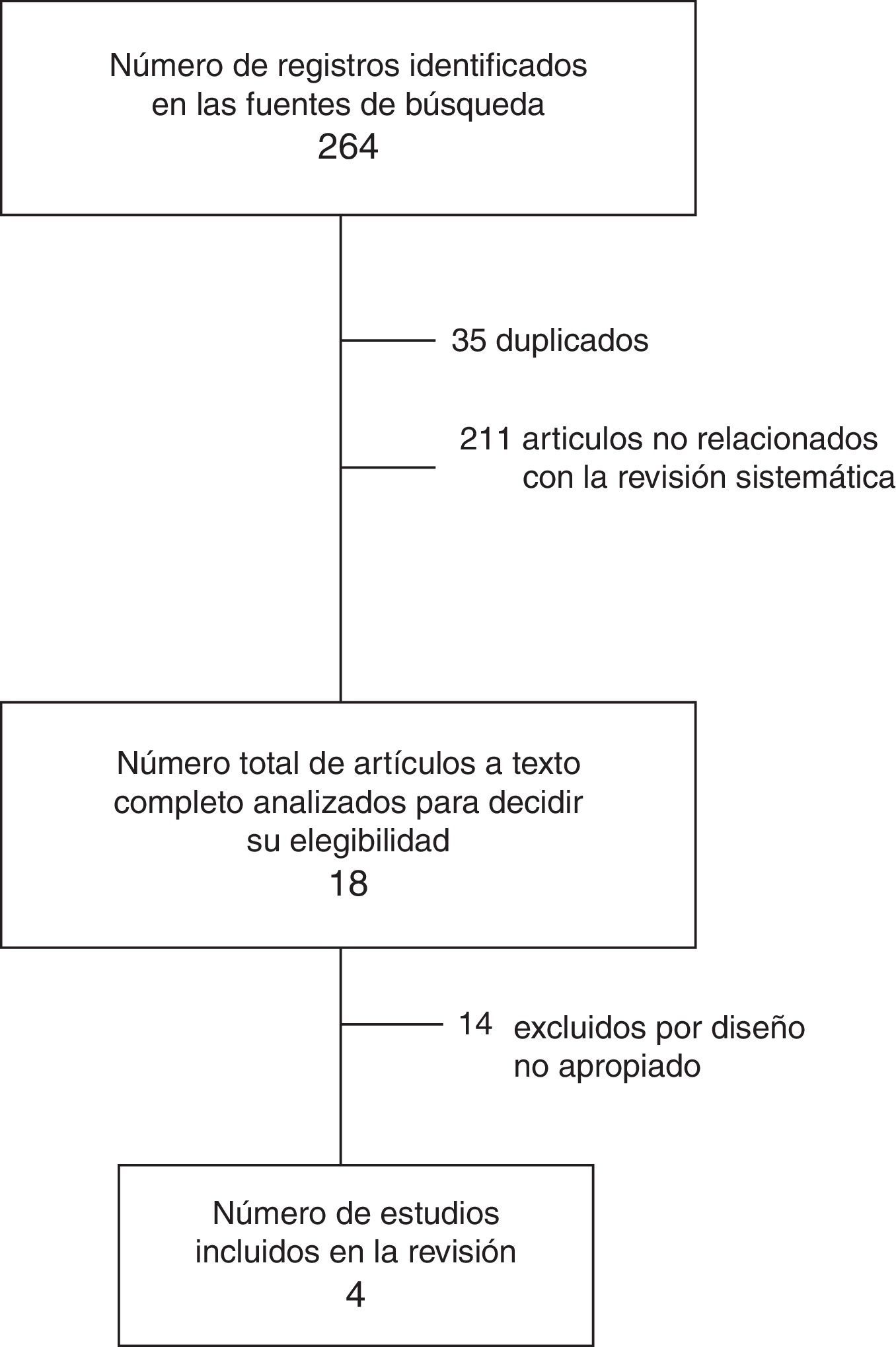
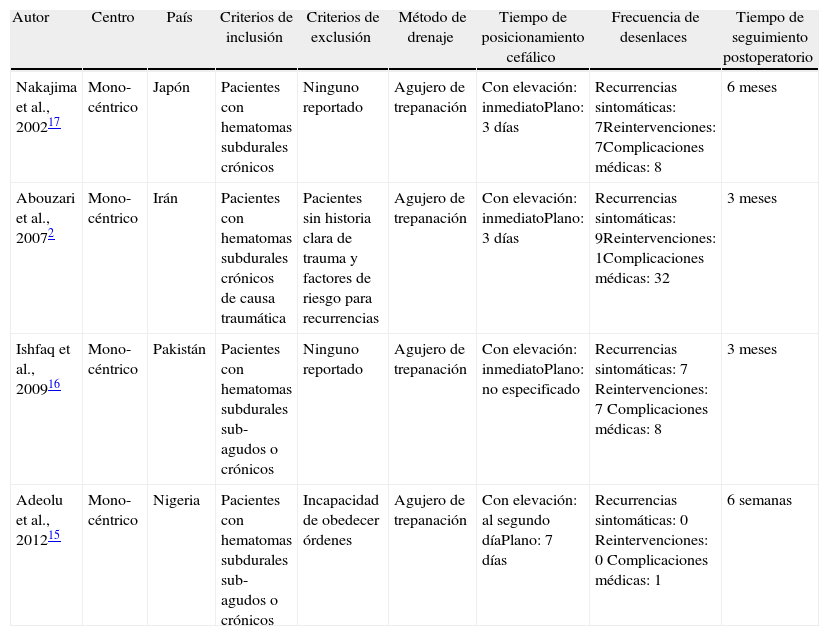
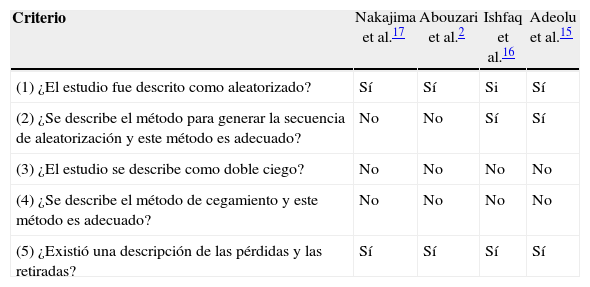
MétodosSe incluyeron todos los estudios prospectivos controlados aleatorizados que analizaron la frecuencia de recurrencias sintomáticas en los pacientes operados por hematomas subdurales crónicos mediante trepanación, con relación al posicionamiento postoperatorio de la cabecera.
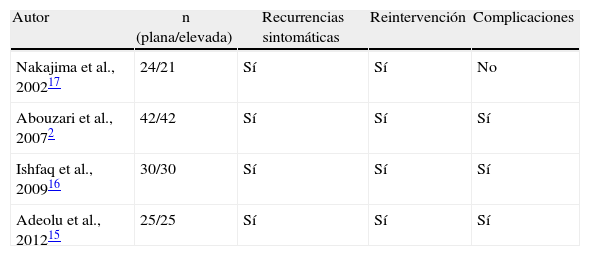
El desenlace primario fueron las recurrencias sintomáticas y los secundarios, las reintervenciones y las complicaciones médicas postoperatorias.
Los resultados se presentaron en riesgos relativos combinados, con sus intervalos de confianza del 95%.
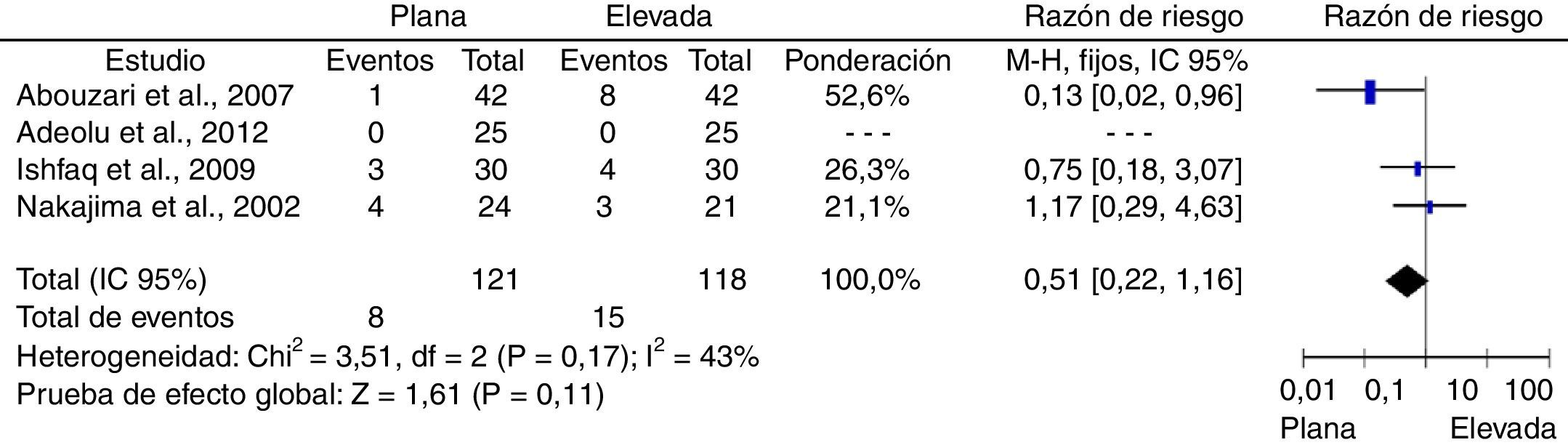
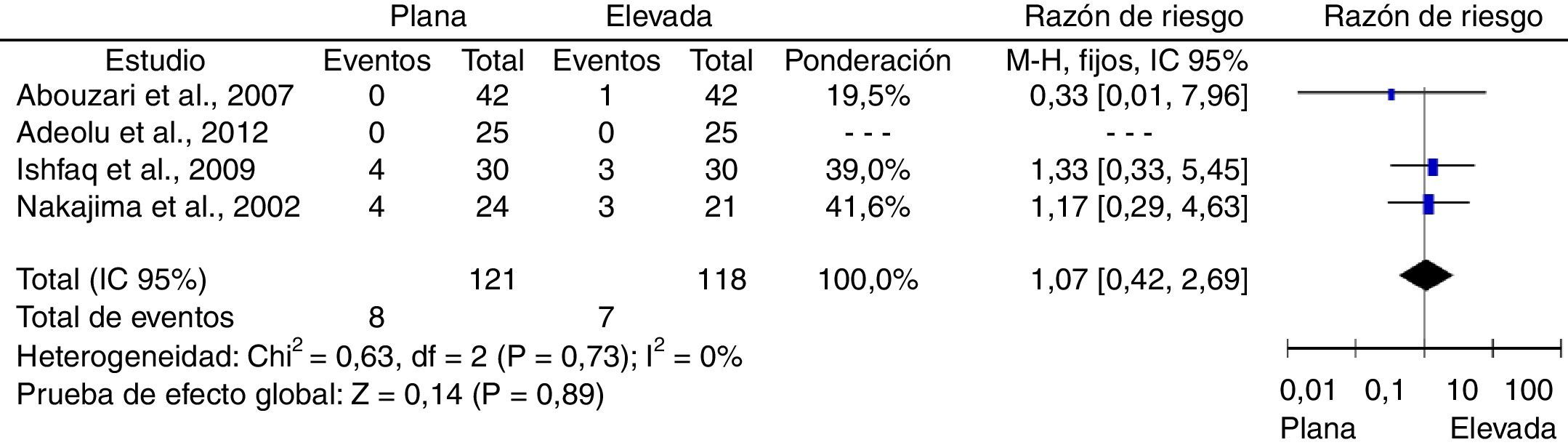
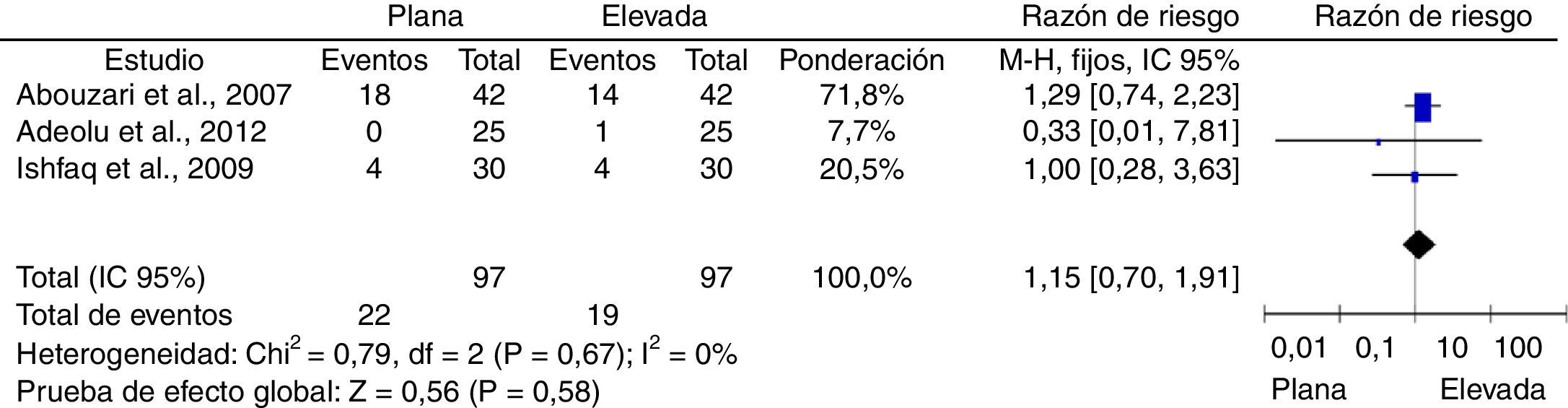
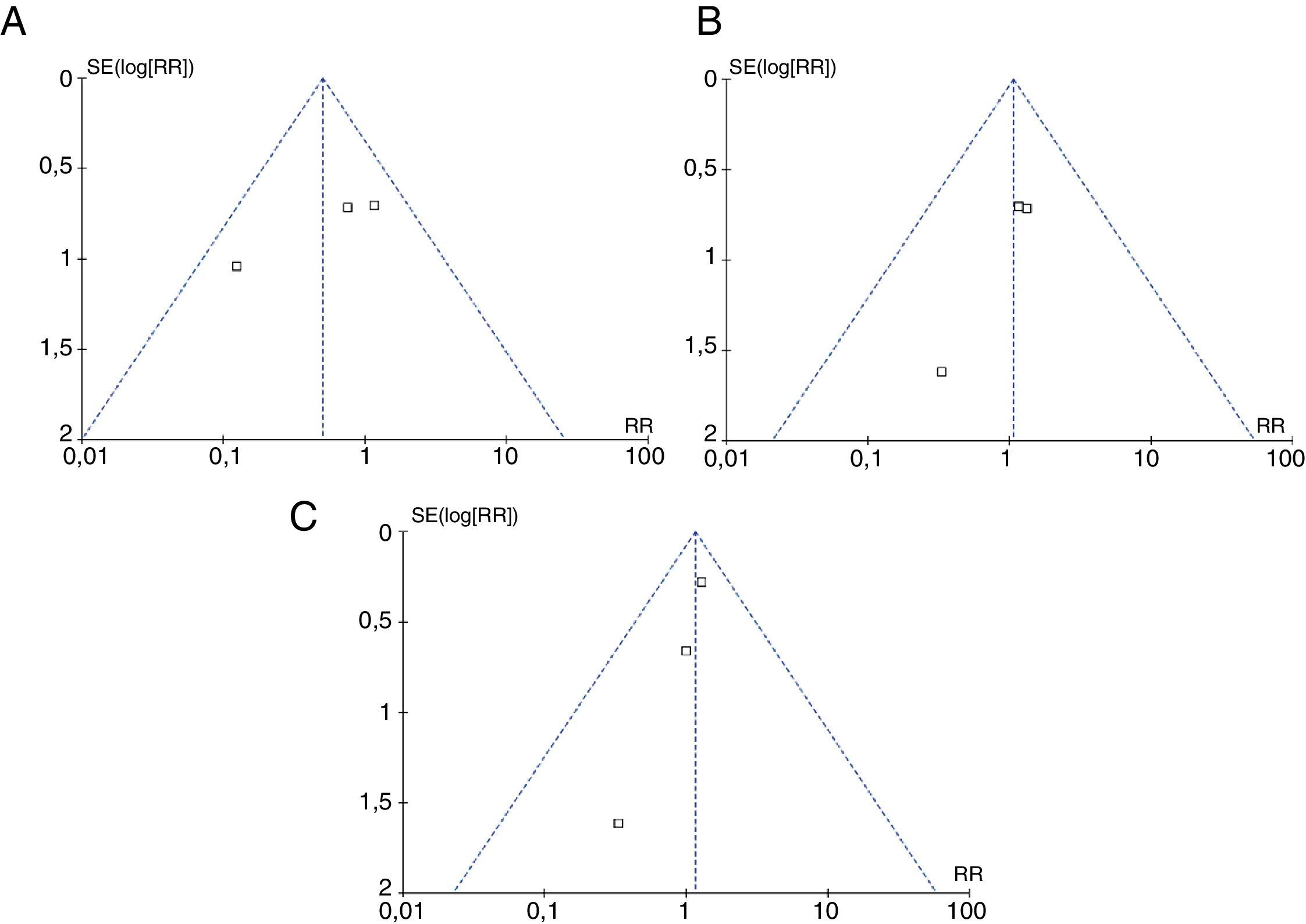
ResultadosFueron incluidos un total de 4 estudios controlados aleatorizados. Los riesgos relativos combinados fueron: recurrencias sintomáticas, 0,51 ([IC95%: 0,22-1,16]; p=0,11); reintervenciones, 1,07 ([IC95%: 0,42-2,69]; p=0,89) y complicaciones, 1,15 ([IC95%: 0,7-1,91]; p=0,58). No se encontró heterogeneidad estadísticamente significativa en ninguno de los análisis.
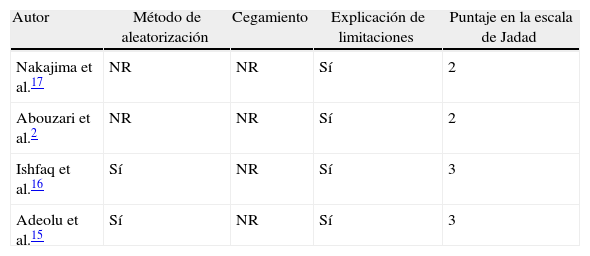
ConclusiónNo se encontraron diferencias en el riesgo de recurrencias sintomáticas, reintervenciones ni complicaciones médicas en los pacientes que fueron mantenidos con la cabecera plana, en comparación con aquellos en quienes fue elevada en el postoperatorio. Aunque los resultados fueron consistentes entre los estudios incluidos, existe un potencial riesgo de sesgos, lo que proscribe emitir recomendaciones definitivas antes de contarse con estudios de mayor calidad metodológica.
Several studies have suggested the possible influence of postoperative bed header position on the risk of symptomatic recurrences and medical complications in patients who have been intervened due chronic subdural haematomas. Nevertheless, this hypothesis has not been assessed by a meta-analysis.
MethodsAll randomised controlled trials analysing symptomatic recurrence rates in patients who underwent burr-hole drainage of chronic subdural haematomas, describing postoperative bed header positioning, were included.
The primary outcome was risk of recurrence and the secondary outcome were the risks of reoperation and medical complications. Results were presented as pooled relative risks, with 95% confidence intervals.
ResultsA total of 4 controlled studies were included. Pooled relative risks were: symptomatic recurrences 0.51 ([95% CI: 0.22-1.16]; P=.11), reoperations, 1.07 ([95% CI: 0.42-2.69]; P=.89) and medical complications, 1.15 ([95% CI: 0.7-1.91]; P=.58). No statistically significant heterogeneity was found in any of the analyses.
ConclusionThere were no differences regarding frequency of symptomatic recurrences, reoperations or medical complications in patients who were maintained in a flat position compared with those whose bed header was elevated during the postoperative course. Despite there being consistency between the results, there is a potential risk of bias; thus proscribing definitive recommendations until studies with higher methodological quality are available.
Article

If it is the first time you have accessed you can obtain your credentials by contacting Elsevier Spain in suscripciones@elsevier.com or by calling our Customer Service at902 88 87 40 if you are calling from Spain or at +34 932 418 800 (from 9 to 18h., GMT + 1) if you are calling outside of Spain.
If you already have your login data, please click here .
If you have forgotten your password you can you can recover it by clicking here and selecting the option ¿I have forgotten my password¿.