The aim of this study is to assess the clinical properties and surgical results of patients diagnosed with spinal schwannomas without neurofibromatosis (NF) properties.
Patients and methodsThe data obtained from 35 patients who underwent resection of spinal schwannomas were analyzed. All cases with neurofibromas and those with a known diagnosis of NF Type 1 or 2 were excluded. 35 patients underwent surgery for spinal schwannoma at our institution between January 1997 and 2010. The data were gathered retrospectively from medical records and included clinical presentation, tumor location and post-operative complications. All cases were surgically excised, and they were confirmed to be schwannomas by pathologists with histopathological sections in paraffin stained with hematoxylin–eosin.
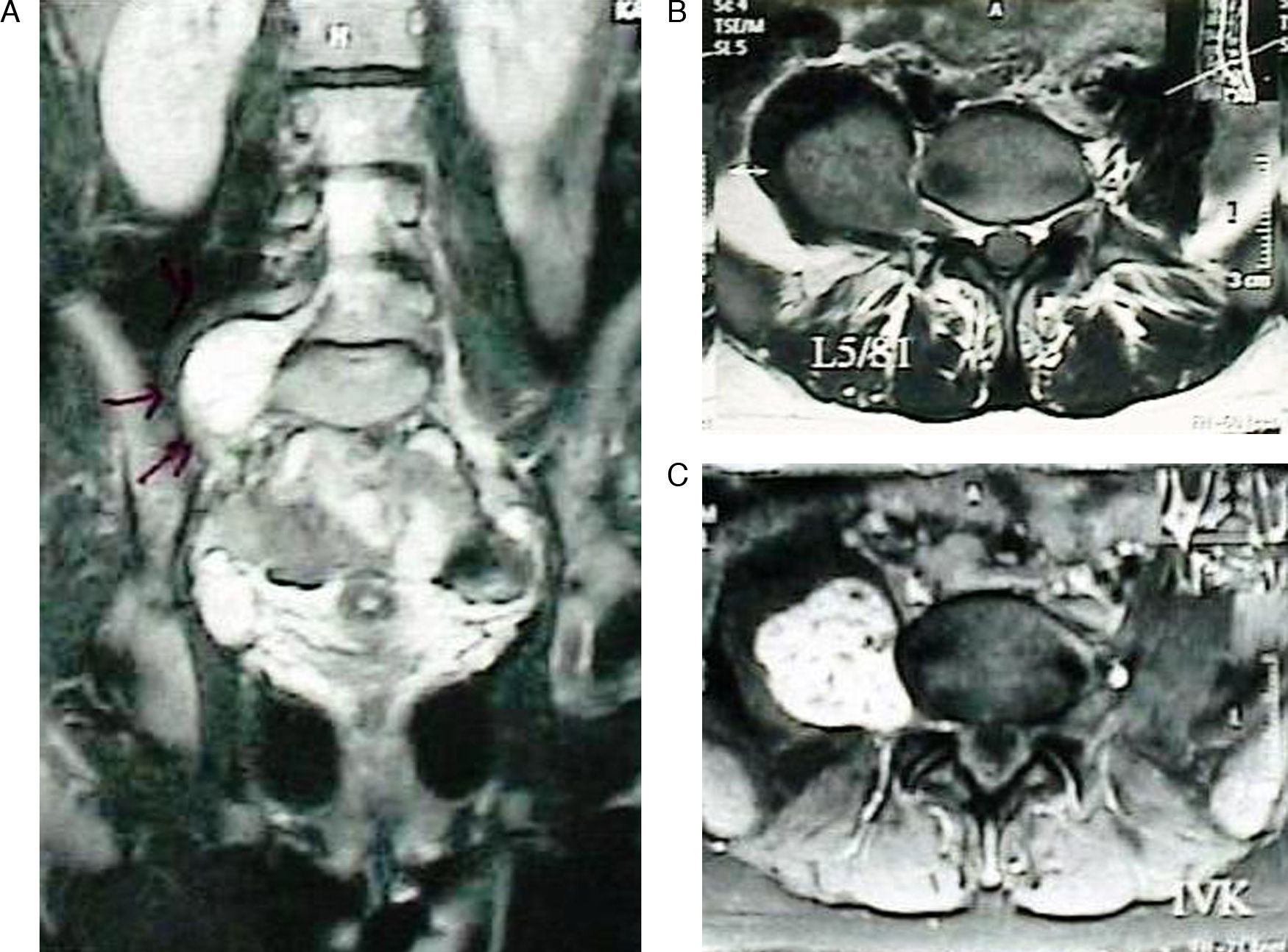
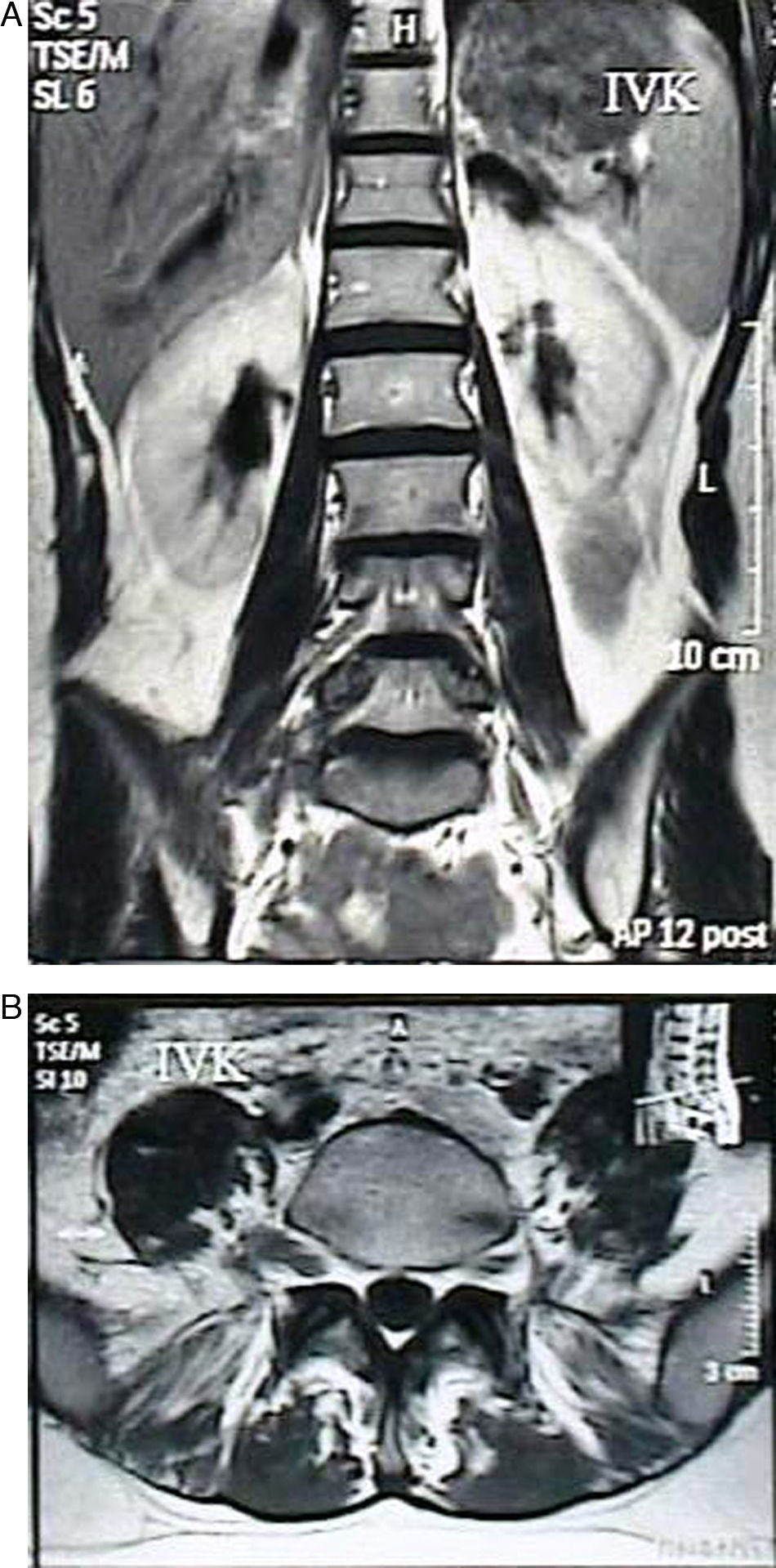
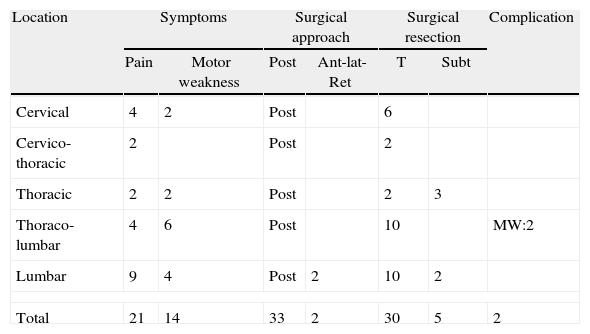
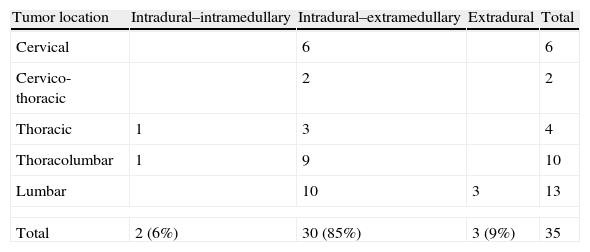
ResultWe treated 35 (20 males and 15 females) patients with spinal schwannomas. The mean age of the patients was 47.2 (between 13 and 76) years. Of the cases, six schwannomas were located in the cervical spine, four in the thoracic spine, two in cervico-thoracic area, 10 in the thoraco-lumbar area and 13 in the lumbar spine. Two patients had malignant schwannomas that were recurrent. Of the 35 cases, the schwannomas were intradural–extramedullary in 30 cases (86%), intradural–intramedullar in 2 cases (6%), and extradural in 3 cases (9%).
ConclusionSpinal schwannomas may occur at any level of the spinal axis and are most frequently intradural–extramedullary. The most common clinical presentation is pain. Most of the spinal schwannomas in non-NF patients can be resected completely without or with minor post-operative deficits. This knowledge may help us to create a strategy for total resection of a spinal schwannomas.
El objetivo de este estudio es evaluar las características clínicas y los resultados quirúrgicos de un grupo de pacientes con diagnóstico de schwannoma medular sin propiedades de neurofibromatosis (NF).
Pacientes y métodosSe analizaron los datos de 35 pacientes sometidos a resección de schwannomas medulares. Todos los casos con neurofibromas y aquellos con un diagnóstico conocido de NF tipo 1 o 2 fueron excluidos del estudio. Los 35 pacientes fueron sometidos a cirugía por schwannoma medular en nuestro centro, entre enero de 1997 y 2010. Los datos obtenidos retrospectivamente de los registros médicos incluyeron la presentación clínica, localización del tumor y complicaciones post-operatorias. Todos los casos fueron extirpados quirúrgicamente, y confirmados como schwannomas mediante especímenes histopatológicos teñidos con hematoxilina-eosina.
ResultadoSe trató a 35 (20 hombres y 15 mujeres) pacientes con schwannomas medulares. La edad media de los pacientes fue de 47,2 años (rango entre 13 y 76). Seis schwannomas se encontraban en la columna cervical, 4 en la columna torácica, 2 en la zona cérvico-torácica, 10 en la zona torácico-lumbar y 13 en la columna lumbar. Dos pacientes sufrieron recurrencias de schwannomas malignos. De los 35 casos, 30 (86%) fueron schwannomas intradurales-extramedulares, 2 (6%) fueron intradurales-intramedulares, y 3 (9%) fueron extradurales.
ConclusiónLos schwannomas medulares pueden aparecer a cualquier nivel de la columna vertebral aunque los más frecuentes son los de localización intradural-extramedular. La presentación clínica más común es el dolor. La mayoría de los schwannomas medulares en pacientes sin NF pueden ser resecados en su totalidad, con o sin secuelas post-operatorias menores. Este conocimiento puede ayudar en la creación de una estrategia para la resección total de schwannomas medulares.
Article

If it is the first time you have accessed you can obtain your credentials by contacting Elsevier Spain in suscripciones@elsevier.com or by calling our Customer Service at902 88 87 40 if you are calling from Spain or at +34 932 418 800 (from 9 to 18h., GMT + 1) if you are calling outside of Spain.
If you already have your login data, please click here .
If you have forgotten your password you can you can recover it by clicking here and selecting the option ¿I have forgotten my password¿.