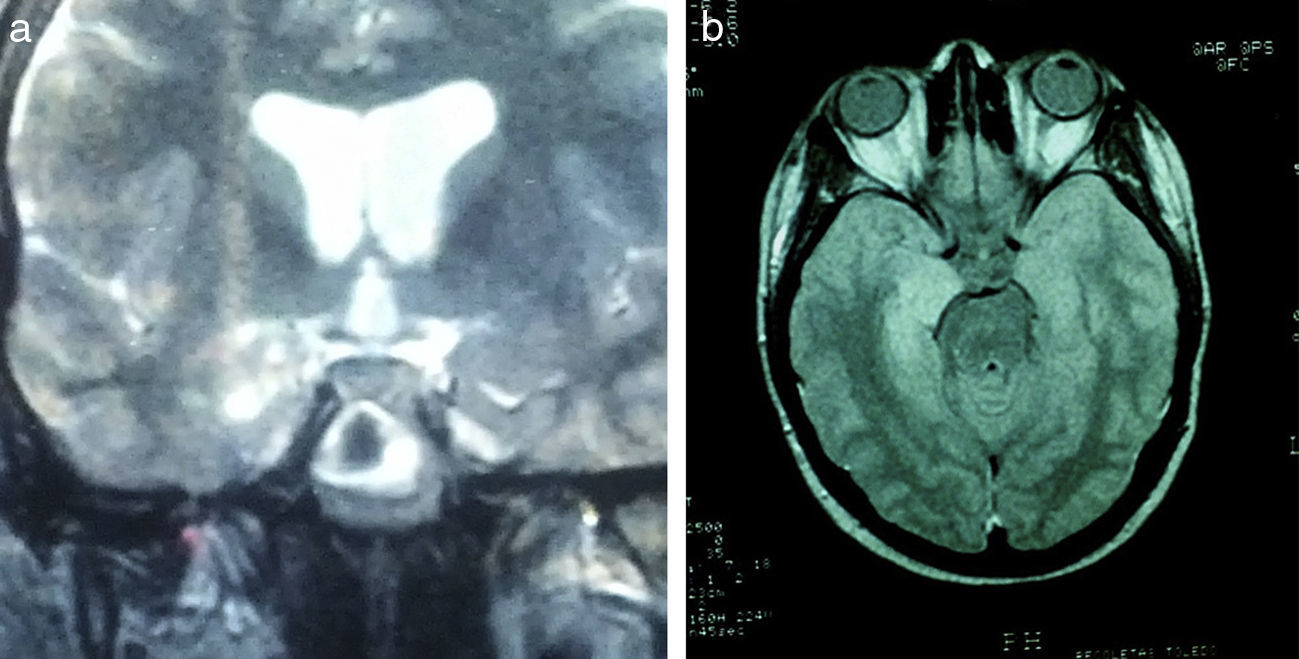
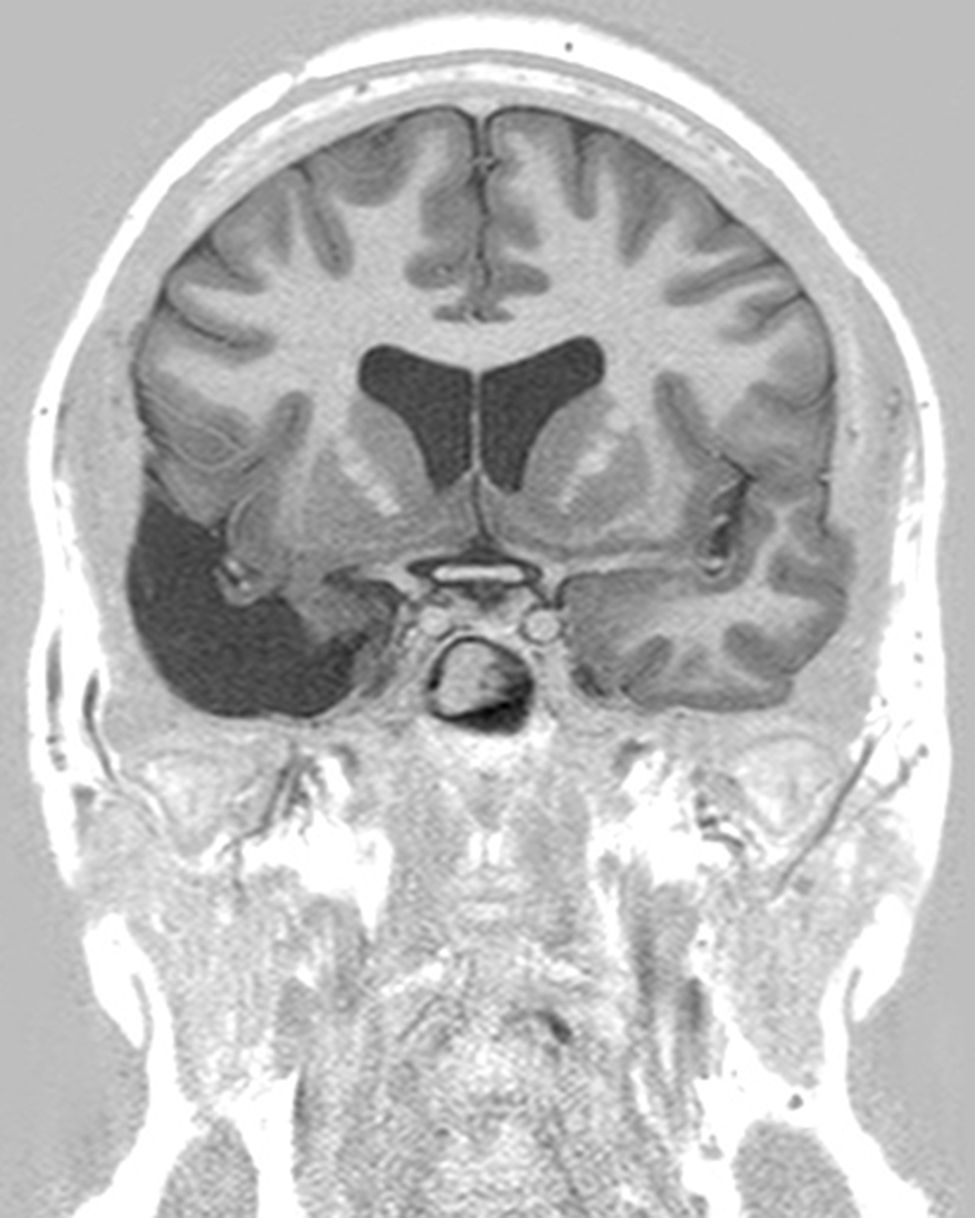
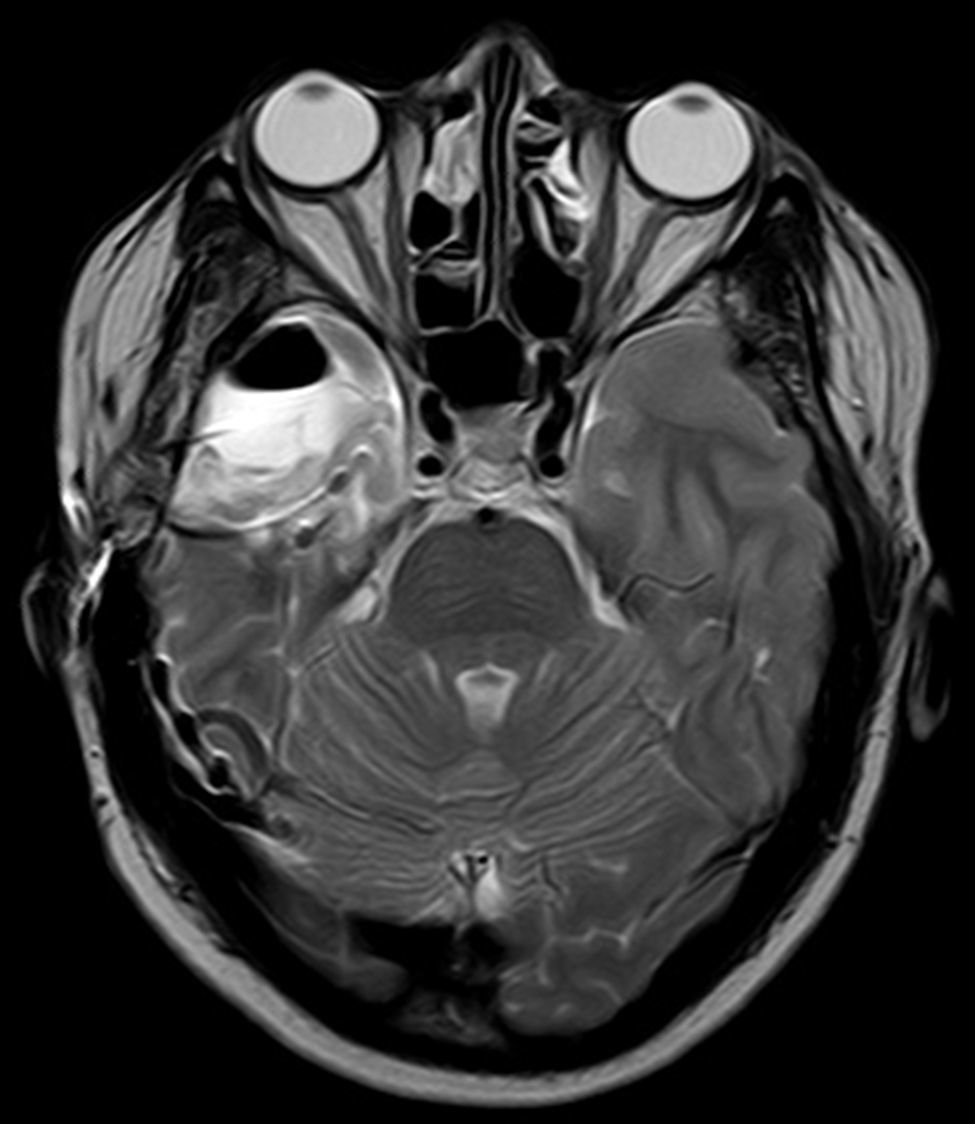
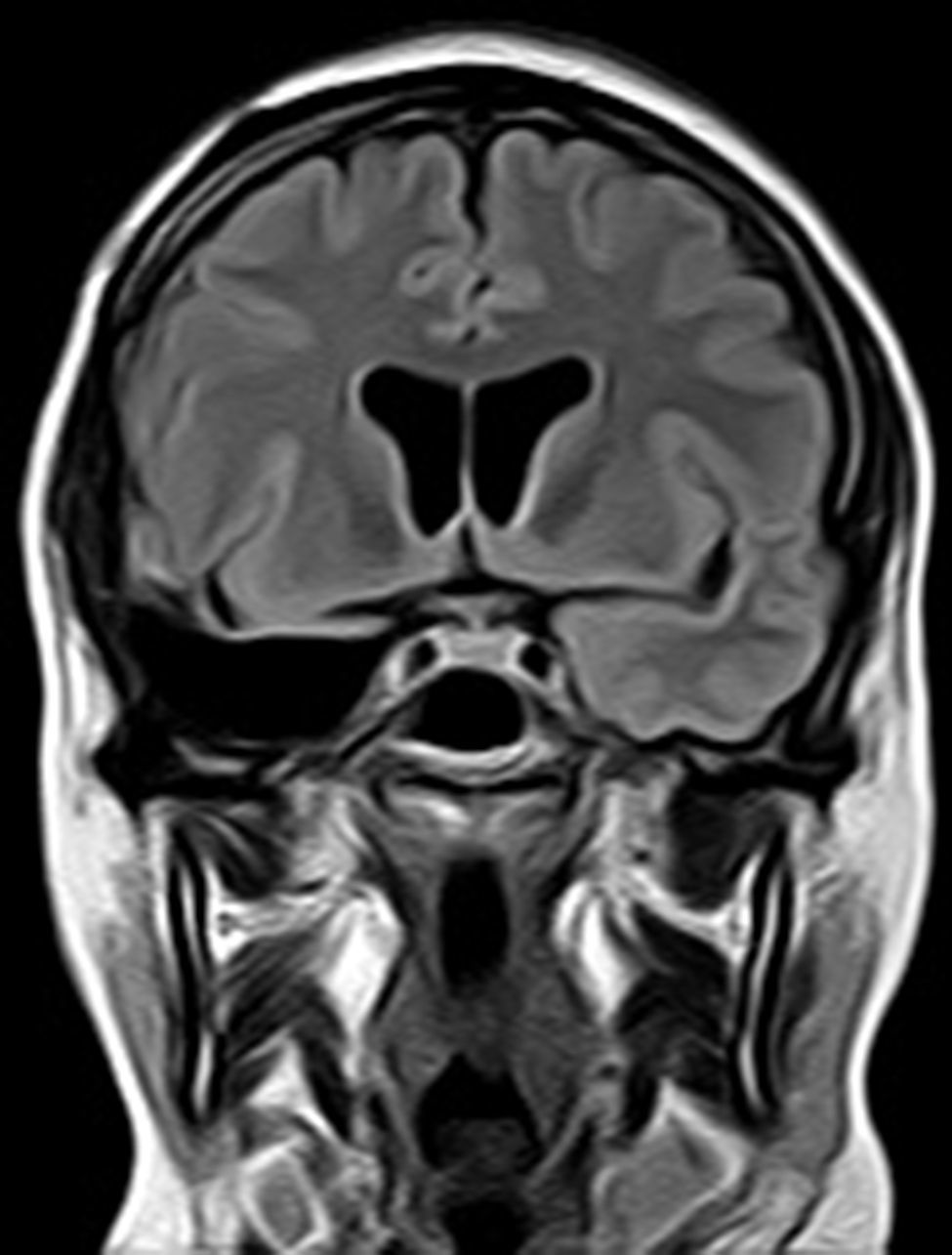
Pese a que desde hace tiempo se conoce que lesiones amigdalares en animales de experimentación producen un modelo de epilepsia, la participación de la amígdala en el complejo de la esclerosis temporal mesial es poco conocida y casi toda la atención se centra en el hipocampo. Este trabajo tiene como propósito enfatizar el papel de la resección de la amígdala para conseguir que el paciente quede sin crisis.
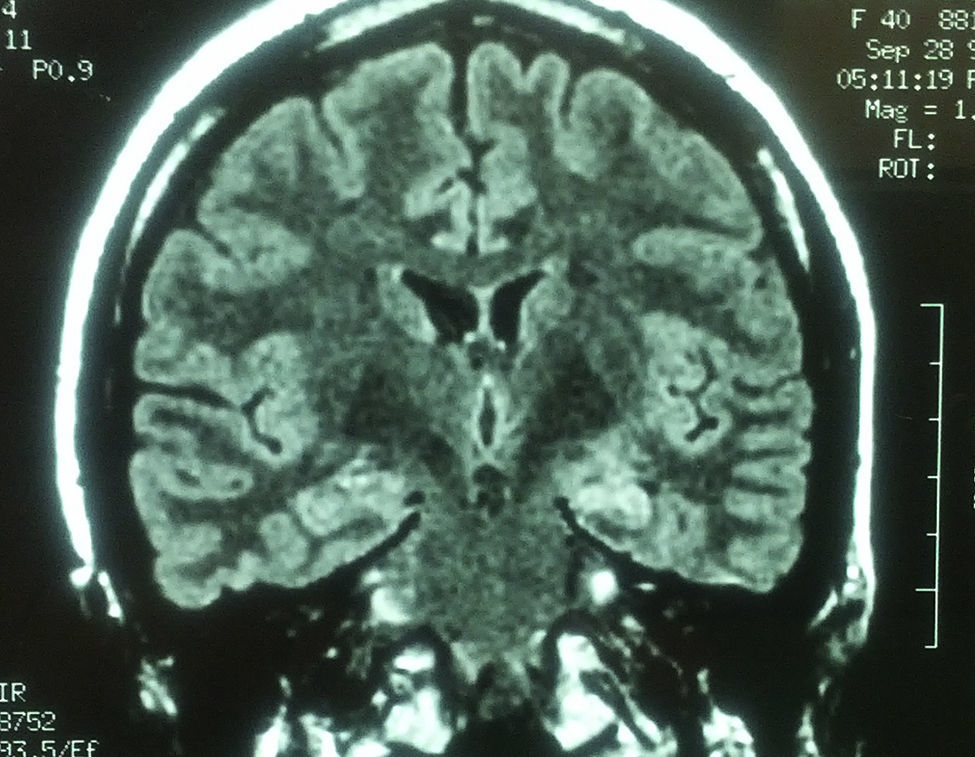
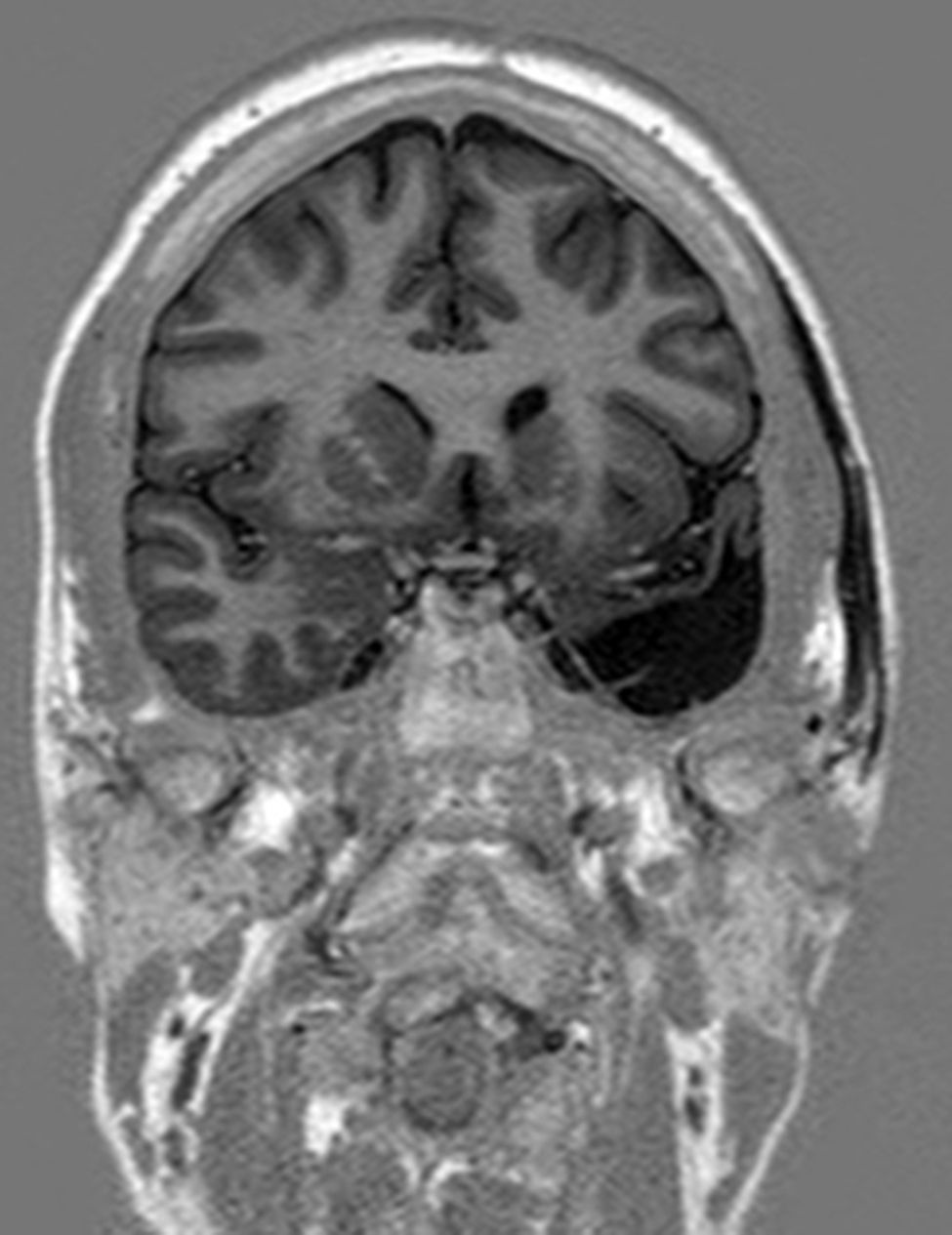
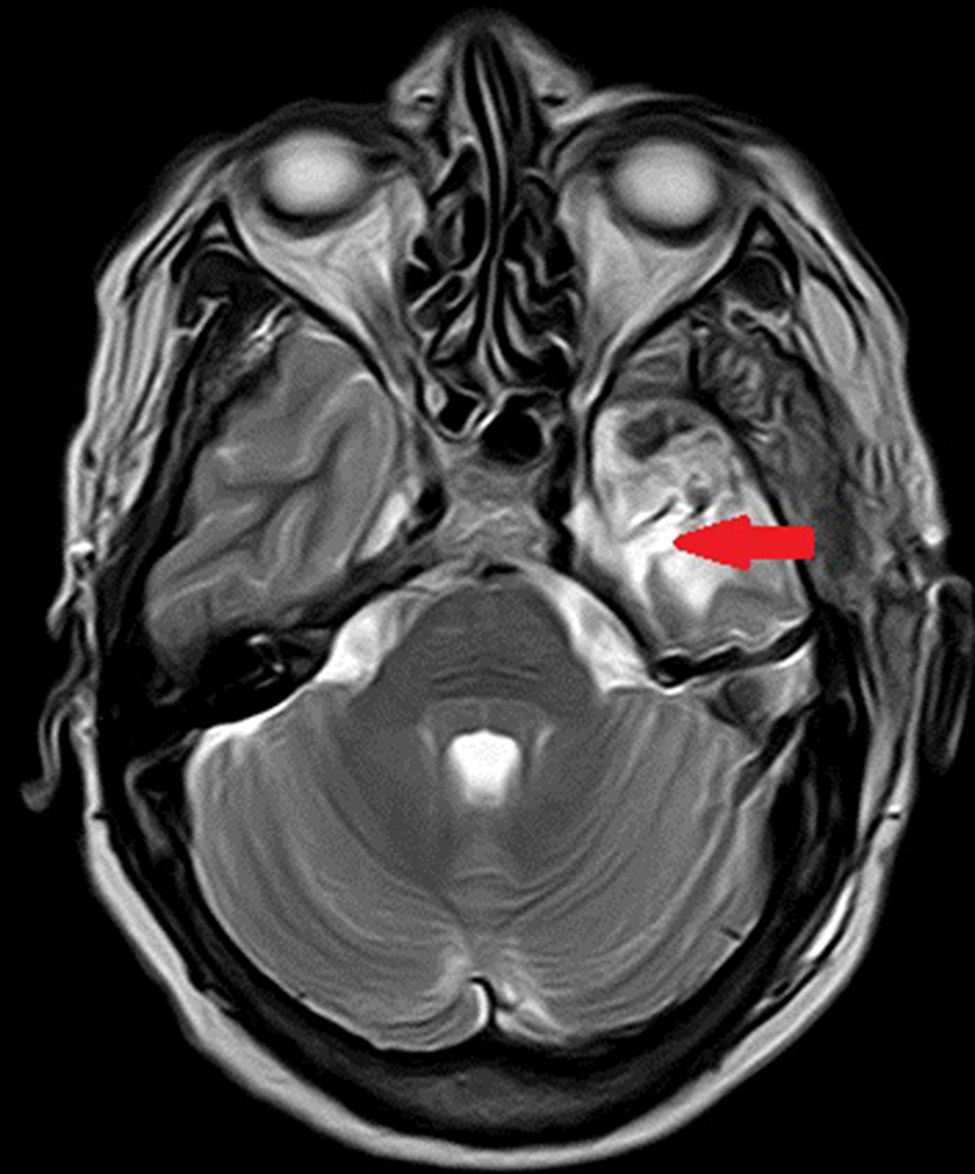
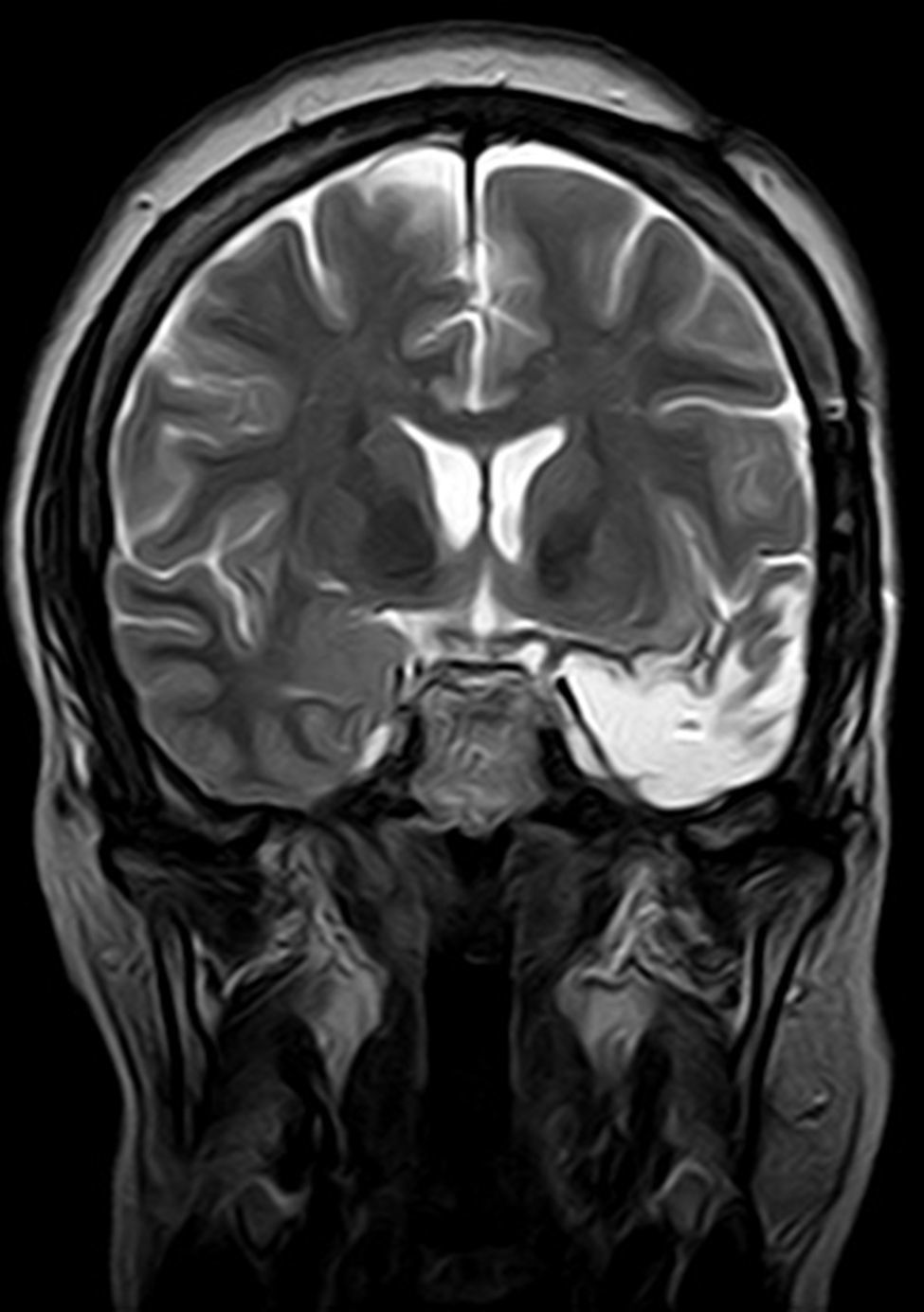
Para ello presentamos dos casos de pacientes mujeres de 50 y 42 años con crisis desde la infancia y diagnosticadas de esclerosis temporal mesial. Ambas fueron intervenidas por nosotros en el año 2000 mediante amigdalohipocampectomía con resección parcial amigdalar más lobectomía temporal izquierda y derecha respectivamente. Las dos pacientes no presentaron nuevas crisis parciales complejas durante los primeros 6 años, empeorando posteriormente por lo que fueron reintervenidas para monitorización con electrodos subdurales y profundos. En ambas se evidenció un inicio ictal compatible con el electrodo situado en la amígdala. La subsiguiente resección del tejido donde se situó el electrodo amigdalar dejó a las dos pacientes libres de crisis.
En estas dos pacientes fue preciso completar la resección amigdalar para conseguir que quedaran libres de crisis. La resección amigdalar es parte importante de la técnica quirúrgica en la epilepsia temporal mesial. Es posible que la amígdala tenga un papel mucho más relevante de lo actualmente considerado en el origen de las crisis.
Even though amygdalar lesions are a known epilepsy model in laboratory animals, the role of the amygdala in mesial temporal sclerosis is not well-known. To date, most interest has been paid to the role of the hippocampal formation. The aim of this article is to emphasize the role of the amygdala in order to render a patient seizure free.
Two patients are presented who were 50 and 42 years old at the time of surgery. They suffered from seizures since childhood and were diagnosed with mesial temporal sclerosis. A temporal lobectomy with hippocampectomy and partial amygdalectomy was performed on both patients in the year 2000, with one patient operated on the right side and the other one on the left side. Both patients were seizure free after surgery for 6 years, but presented again with seizures after that time. They were evaluated again for surgery, and subdural grids were placed, together with a deep electrode in the remnants of the amygdala. The amygdalar electrode showed to be the seizure onset in the two cases, and its resection rendered both patients seizure free.
These two patients show that a complete amygdalar resection is necessary to render some patients seizure free. It might be the amygdala has a greater role than previously thought.
Article

If it is the first time you have accessed you can obtain your credentials by contacting Elsevier Spain in suscripciones@elsevier.com or by calling our Customer Service at902 88 87 40 if you are calling from Spain or at +34 932 418 800 (from 9 to 18h., GMT + 1) if you are calling outside of Spain.
If you already have your login data, please click here .
If you have forgotten your password you can you can recover it by clicking here and selecting the option ¿I have forgotten my password¿.